A faulty brake pedal position sensor (BPPS) can lead to a host of issues, from erratic braking to complete brake failure. Using a Scan Tool To Calibrate Brake Pedal Position Sensor is often the most effective way to diagnose and resolve these problems. This article provides a detailed guide on how to use a scan tool for BPPS calibration, covering everything from understanding the sensor’s function to troubleshooting common issues.
Modern vehicles rely heavily on electronic systems, and the braking system is no exception. The BPPS plays a crucial role in determining the driver’s braking intent and communicating that information to the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU). If the BPPS malfunctions or provides inaccurate readings, it can compromise the safety and performance of the braking system. Having a scan tool, such as those used for a 2011 Honda Pilot throttle body relearn with scan tool, can be invaluable for diagnosing these complex electronic systems.
Understanding the Brake Pedal Position Sensor
The BPPS is a variable resistor that changes its resistance based on the position of the brake pedal. When the pedal is released, the resistance is high, and when the pedal is depressed, the resistance decreases. This change in resistance is translated into a voltage signal that the ECU uses to determine the driver’s braking input. This signal is crucial for various systems, including:
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): The BPPS signal helps the ABS module determine when to activate and modulate brake pressure to prevent wheel lockup.
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): The BPPS input is used by the ESC system to determine if the driver is applying the brakes while the vehicle is losing control, allowing the system to intervene and stabilize the vehicle.
- Traction Control System (TCS): Similar to ESC, the TCS uses the BPPS signal to detect wheel slip during acceleration and adjust engine power and braking force accordingly.
- Cruise Control: The BPPS signal disengages the cruise control when the brake pedal is pressed.
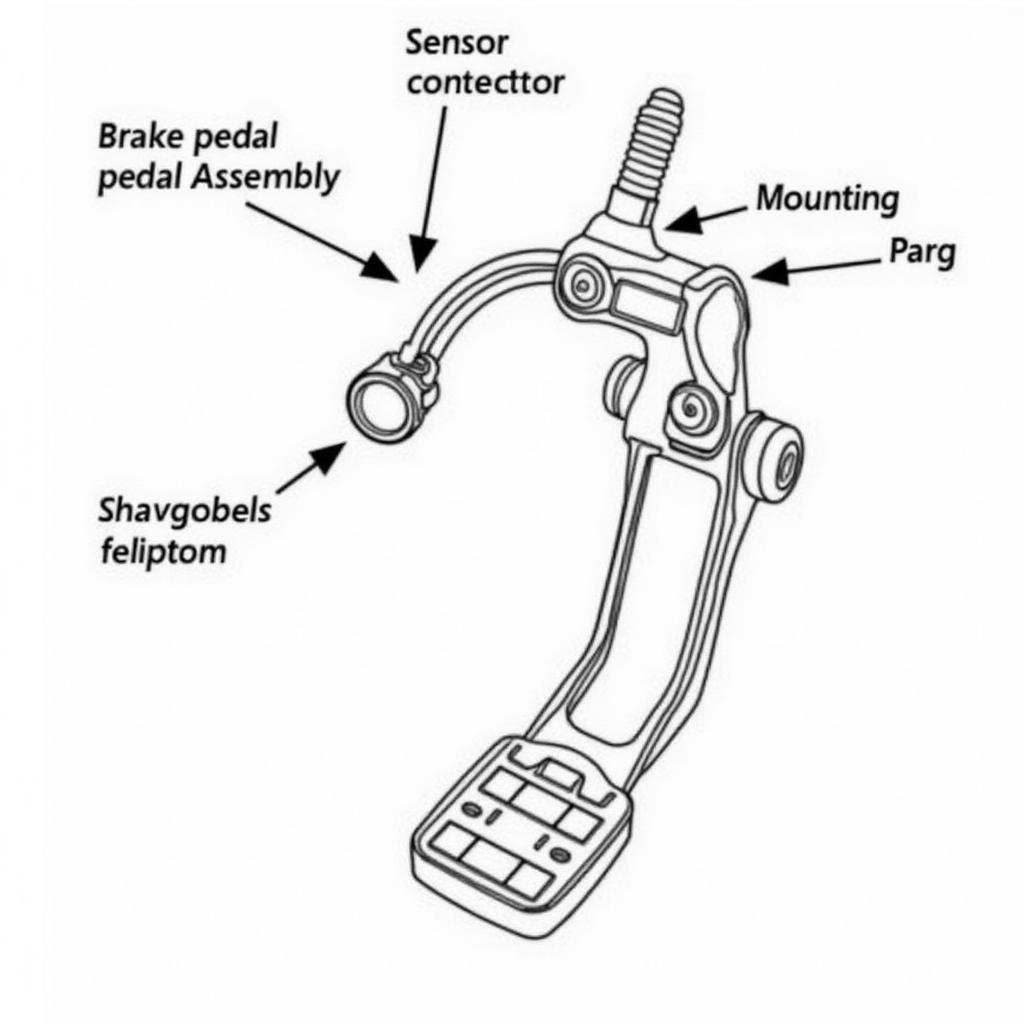 Brake Pedal Position Sensor Location Diagram
Brake Pedal Position Sensor Location Diagram
Why Use a Scan Tool for BPPS Calibration?
Using a scan tool to calibrate brake pedal position sensor provides several advantages. A scan tool allows you to:
- Read and Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): A scan tool can retrieve specific DTCs related to the BPPS, helping pinpoint the exact problem.
- Monitor Live Data: You can observe real-time BPPS data, such as voltage and resistance, to identify discrepancies and inconsistencies.
- Perform Calibration Procedures: Many modern vehicles require specific calibration procedures for the BPPS after replacement or adjustment. A scan tool is essential for executing these procedures.
- Access Advanced Diagnostics: Some scan tools offer advanced diagnostic functions, like actuator tests and bidirectional control, allowing for a more thorough assessment of the BPPS and related systems.
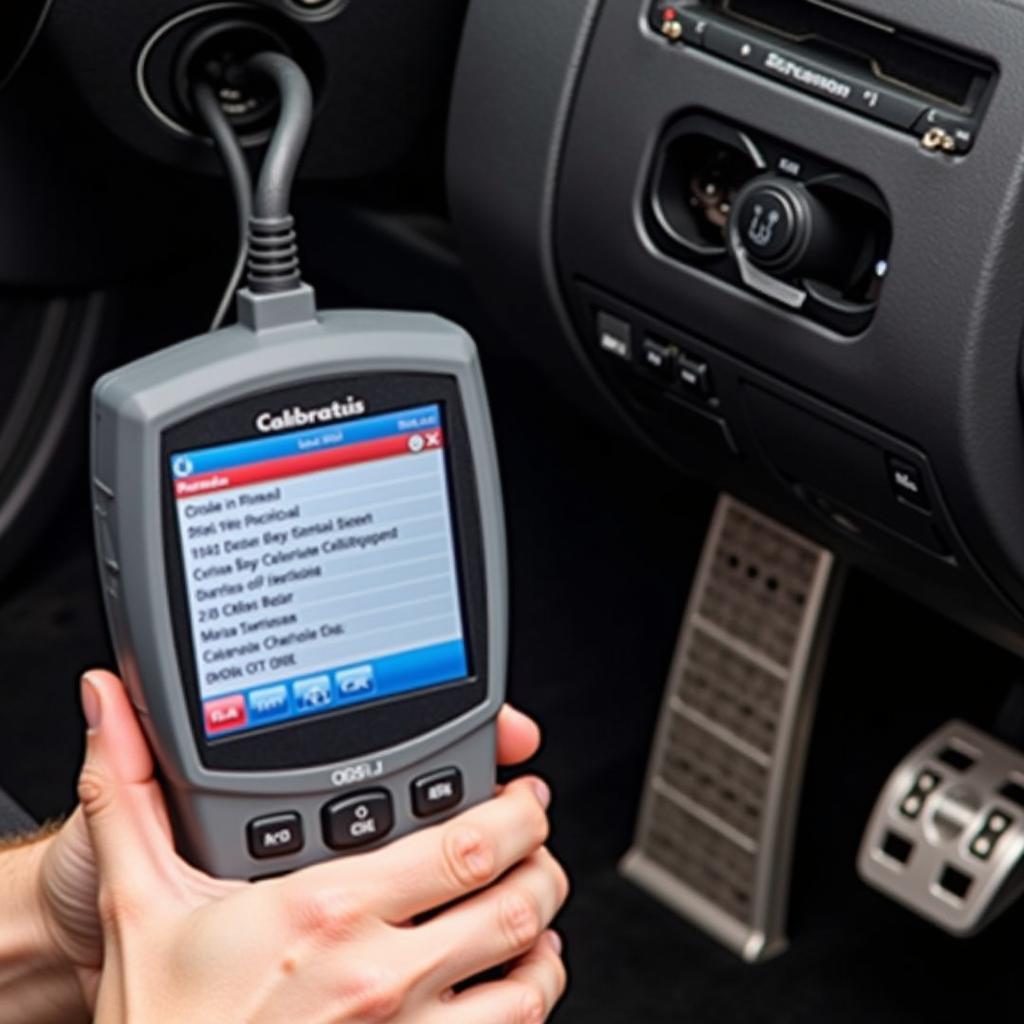 Scan Tool Calibrating Brake Pedal Position Sensor
Scan Tool Calibrating Brake Pedal Position Sensor
How to Calibrate the BPPS with a Scan Tool
While the specific steps vary depending on the vehicle make and model, the general procedure involves:
- Connect the Scan Tool: Plug the scan tool into the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Turn the Ignition On: Turn the ignition key to the “On” position without starting the engine.
- Access the ABS Module: Using the scan tool, navigate to the ABS module.
- Select BPPS Calibration: Choose the option for BPPS calibration or relearn.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: The scan tool will guide you through the specific calibration steps for your vehicle. This may involve depressing and releasing the brake pedal a certain number of times or holding the pedal at a specific position.
- Clear DTCs: After the calibration is complete, clear any stored DTCs related to the BPPS.
It’s also helpful to have a parking brake scan tool handy for diagnosing any potential issues with your parking brake system.
Troubleshooting Common BPPS Issues
- Intermittent BPPS Signal: This can be caused by a loose connection, damaged wiring, or a faulty sensor. Check the wiring harness and connector for damage.
- Inaccurate BPPS Readings: A misaligned sensor, worn pedal components, or a faulty sensor can lead to inaccurate readings. Inspect the sensor’s mounting and alignment.
- No BPPS Signal: This indicates a complete failure of the sensor or a wiring issue. Test the sensor’s resistance and continuity.
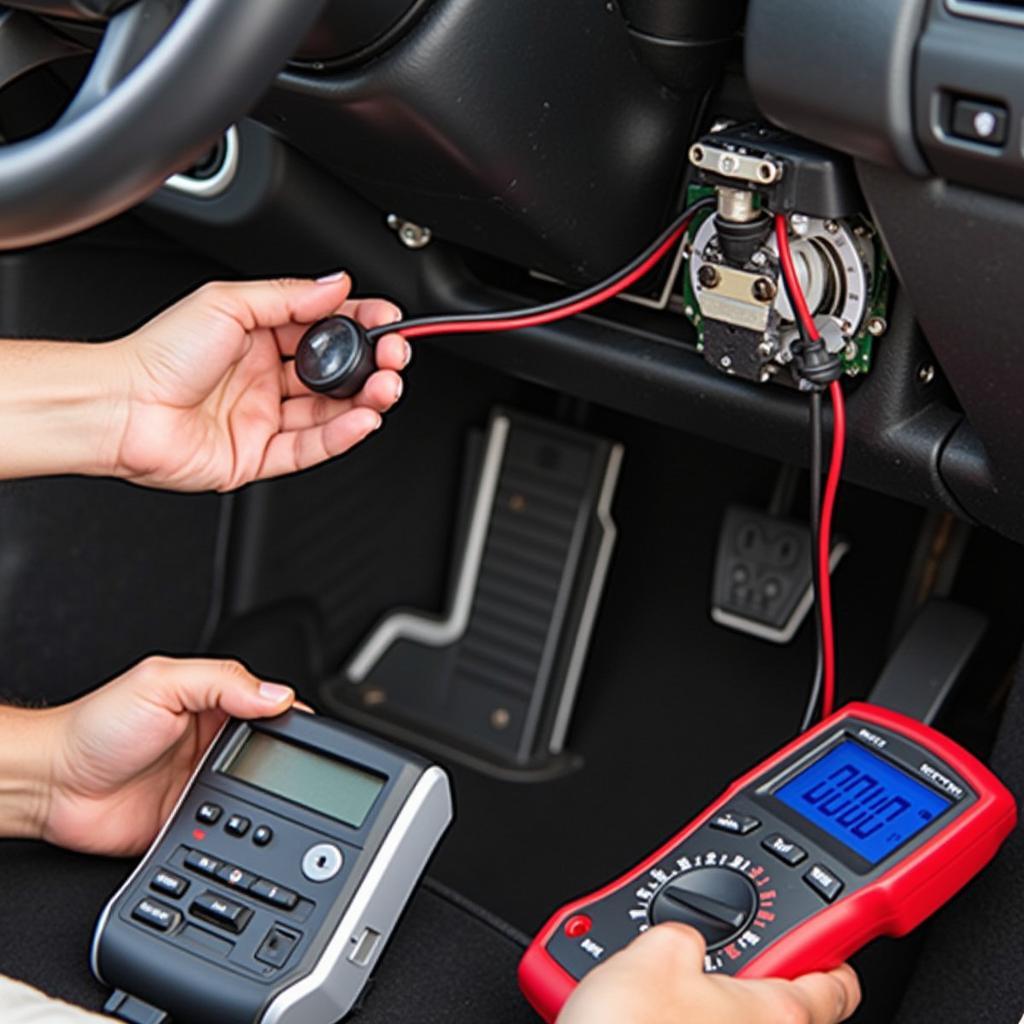 Technician Diagnosing Brake Pedal Position Sensor Issues
Technician Diagnosing Brake Pedal Position Sensor Issues
Conclusion
Using a scan tool to calibrate brake pedal position sensor is a vital skill for any automotive technician or informed car owner. A properly functioning BPPS is essential for the safe and efficient operation of modern braking systems. By understanding the sensor’s function and utilizing a scan tool for diagnosis and calibration, you can effectively address BPPS-related problems and ensure optimal braking performance. For any further assistance or inquiries, please contact ScanToolUS at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1615 S Laramie Ave, Cicero, IL 60804, USA.
FAQ
- Can I calibrate the BPPS without a scan tool? Some older vehicles may allow for manual adjustment, but most modern vehicles require a scan tool for proper calibration.
- How often should I calibrate the BPPS? Typically, calibration is necessary after sensor replacement or adjustment, or when a related DTC is present.
- What are the symptoms of a faulty BPPS? Symptoms include erratic braking, illuminated brake warning lights, ABS or ESC malfunction, and cruise control issues.
- Can a faulty BPPS cause brake failure? While rare, a severely malfunctioning BPPS can contribute to braking system issues, potentially leading to reduced braking performance.
- Where can I purchase a scan tool suitable for BPPS calibration? Reputable automotive tool suppliers and online retailers offer a wide selection of scan tools.
- What are some other uses of a scan tool for brake system diagnosis? Scan tools can be used to diagnose issues with the ABS module, wheel speed sensors, and other brake system components.
- Is it difficult to use a scan tool for BPPS calibration? Most scan tools are user-friendly and provide step-by-step instructions for calibration procedures.