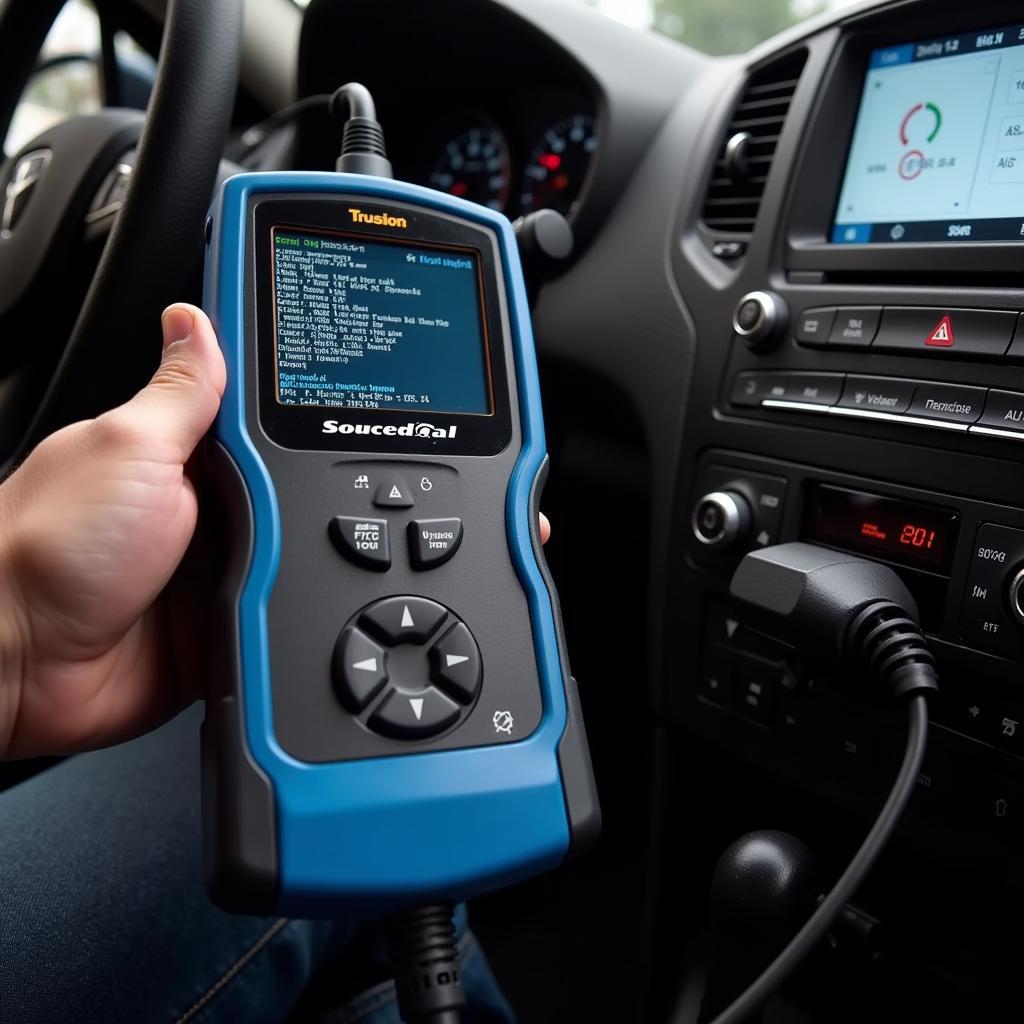
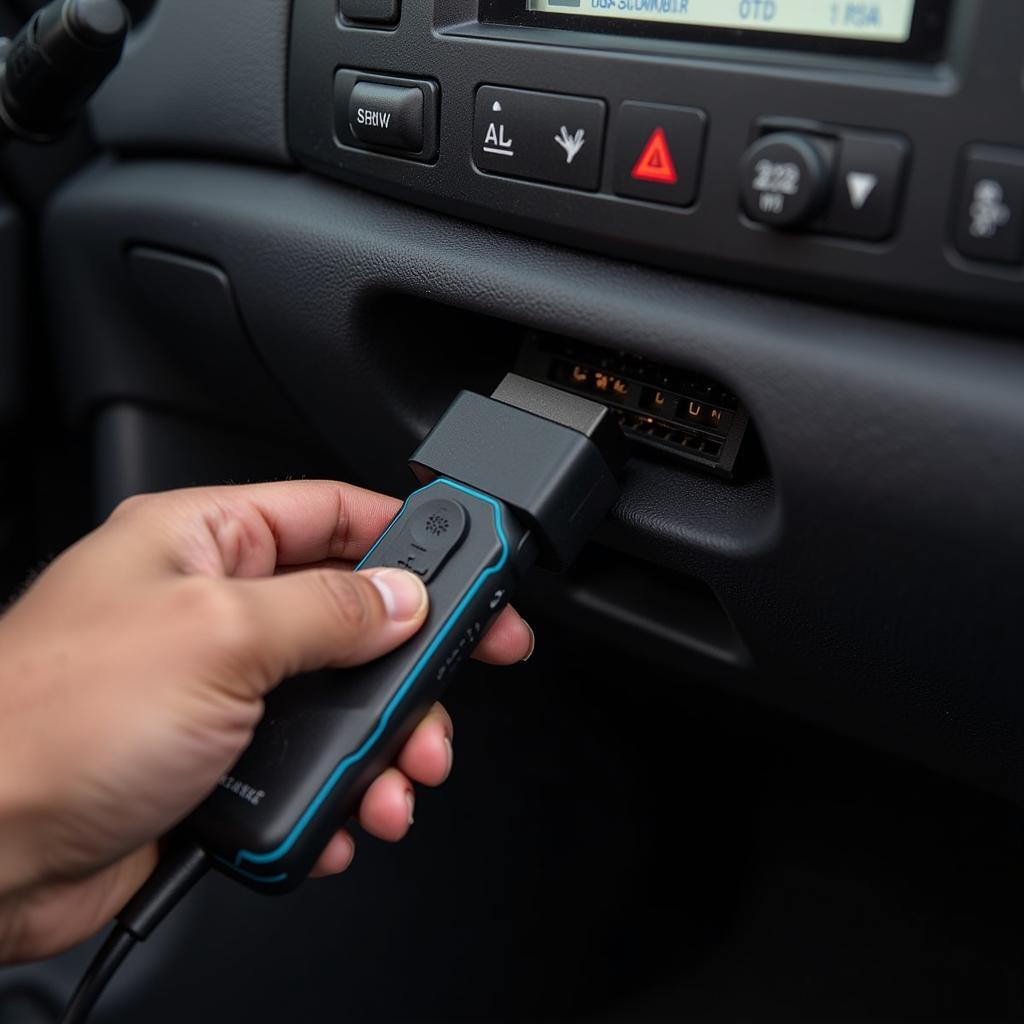
The diagnostic tool 1.63 is a powerful device that can help you identify and troubleshoot problems with your car. Whether you’re a car owner, mechanic, or technician, understanding how to use this tool effectively can save you time and money. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process step by step.
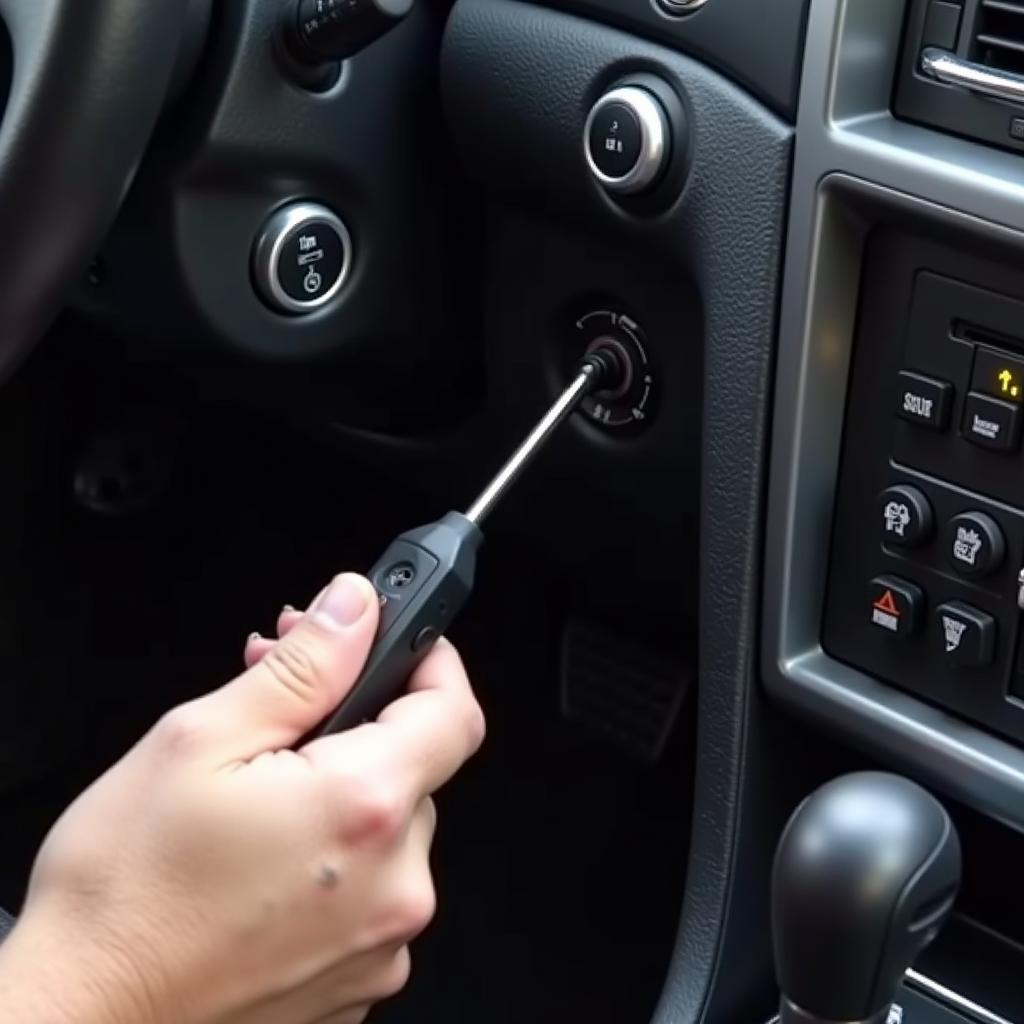 Connecting Diagnostic Tool 1.63
Connecting Diagnostic Tool 1.63
Understanding Diagnostic Tool 1.63
Before diving into the how-to, let’s first understand what this tool is all about. Diagnostic tool 1.63 is a specific version of OBD2 scanners, designed to interface with your car’s onboard computer system. It retrieves Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), essentially error codes stored in your vehicle’s computer, which indicate potential issues.
Preparing for Diagnosis
- Locate your car’s OBD-II port: This port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn off your engine and all accessories: This ensures accurate readings.
- Connect the diagnostic tool 1.63 to the OBD-II port.
Using Diagnostic Tool 1.63
- Turn on the ignition: Don’t start the engine yet. This powers up the diagnostic tool.
- Follow the on-screen prompts: The tool will guide you through the process of reading and clearing codes.
- Reading DTCs:
- Select the “Read Codes” option on the tool.
- The tool will display any stored DTCs.
- Note down the codes for further research.
- Understanding DTCs:
- Refer to a reliable source, like the diagnostic tool 1.63 manual, to decipher the meaning of each code.
- Clearing DTCs:
- After addressing the underlying issue related to a code, you can clear it from the system.
- Select the “Clear Codes” option on the tool.
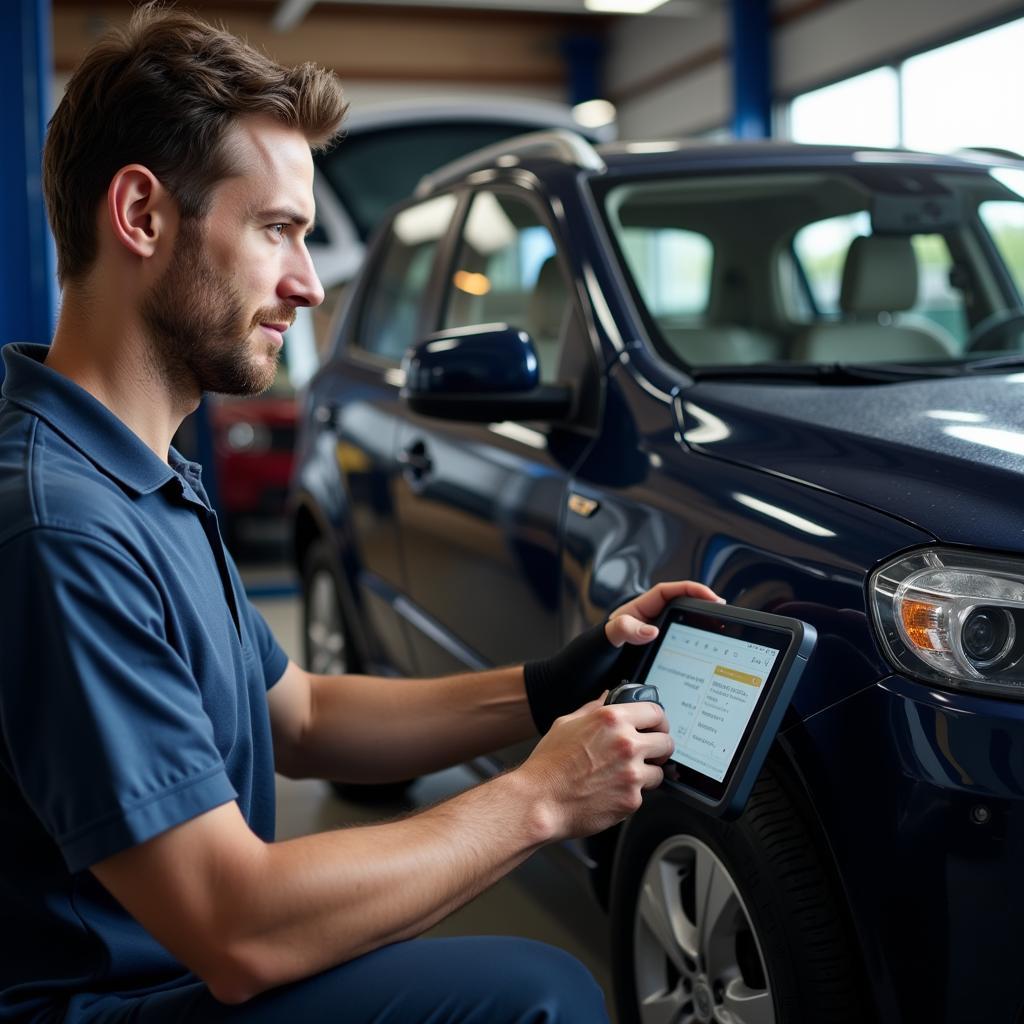 Mechanic Using Diagnostic Tool 1.63
Mechanic Using Diagnostic Tool 1.63
Common Uses of Diagnostic Tool 1.63
- Check Engine Light: Diagnose the reason behind the check engine light illumination.
- Sensor Data: Monitor live data from various sensors, including oxygen sensors, MAF sensor, and more.
- Emissions Testing: Check if your vehicle is ready for emissions testing.
- Component Testing: Activate certain components, like fuel injectors or solenoids, for testing purposes.
Tips for Effective Use
- Invest in a quality tool: While many options are available, a reliable diagnostic tool 1.63 ensures accurate readings and long-term use.
- Update the tool regularly: Manufacturers often release updates to improve functionality and add features.
- Keep a record of codes: Maintaining a log of past codes and their solutions can be helpful for future reference.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Tool Not Powering On: Check the connection to the OBD-II port and ensure the ignition is on.
- Communication Errors: Try disconnecting and reconnecting the tool. If the problem persists, there might be an issue with the vehicle’s OBD-II system.
- Incorrect Readings: Ensure the tool is updated to the latest version and compatible with your car model.
 Car Diagnostic Report on Screen
Car Diagnostic Report on Screen
“Regularly using a diagnostic tool like the 1.63 model allows car owners to stay ahead of potential issues,” says John Miller, a senior automotive engineer at ScanToolUS. “It’s like having a window into your car’s health, helping you address minor problems before they escalate.”
Conclusion
Understanding How To Use Diagnostic Tool 1.63 can empower you to take control of your car’s maintenance. By following the steps outlined in this guide and utilizing the tool’s capabilities, you can diagnose issues accurately and potentially save on costly repairs. Remember to always refer to reliable sources for interpreting DTCs and consult with a qualified mechanic for complex problems. For expert assistance, feel free to connect with us at ScanToolUS, +1 (641) 206-8880, 1615 S Laramie Ave, Cicero, IL 60804, USA.


