Understanding car scanner codes is crucial for both car owners and professional mechanics. These codes, appearing as a jumble of letters and numbers, hold the key to diagnosing and fixing your vehicle’s issues. This guide provides a complete walkthrough on how to interpret these codes, empowering you to take control of your car’s maintenance.
Similar to the Kobra OBD2 scanner car code reader, many code readers offer straightforward interpretations. However, a deeper understanding of the process enhances your troubleshooting abilities.
Car scanner codes, also known as Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), are generated by your car’s onboard diagnostic system (OBD-II). When a malfunction is detected, the system stores a corresponding code, which can then be retrieved using an OBD-II scanner. Knowing how to read these codes can save you time and money, avoiding unnecessary trips to the mechanic.
Understanding the Structure of Car Scanner Codes
Each code follows a specific structure, providing valuable information about the nature of the problem. The standardized five-character alphanumeric code, often starting with a letter, allows for precise identification across different vehicle makes and models.
What Does Each Character Mean?
The first character represents the system where the fault is detected:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, etc.)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows, etc.)
- C: Chassis (ABS, steering, etc.)
- U: Network & Vehicle Integration (modules communication)
The second character indicates the code type:
- 0: Generic (standardized across all manufacturers)
- 1: Manufacturer-specific (codes unique to the carmaker)
The third character identifies the specific subsystem within the broader category (e.g., fuel system, ignition system, etc.).
The fourth and fifth characters specify the exact fault within that subsystem.
How to Read Car Scanner Codes Using a Scanner
Obtaining the codes is straightforward. Plug the OBD-II scanner into the port located under the dashboard, usually on the driver’s side. Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine. The scanner will then retrieve any stored codes.
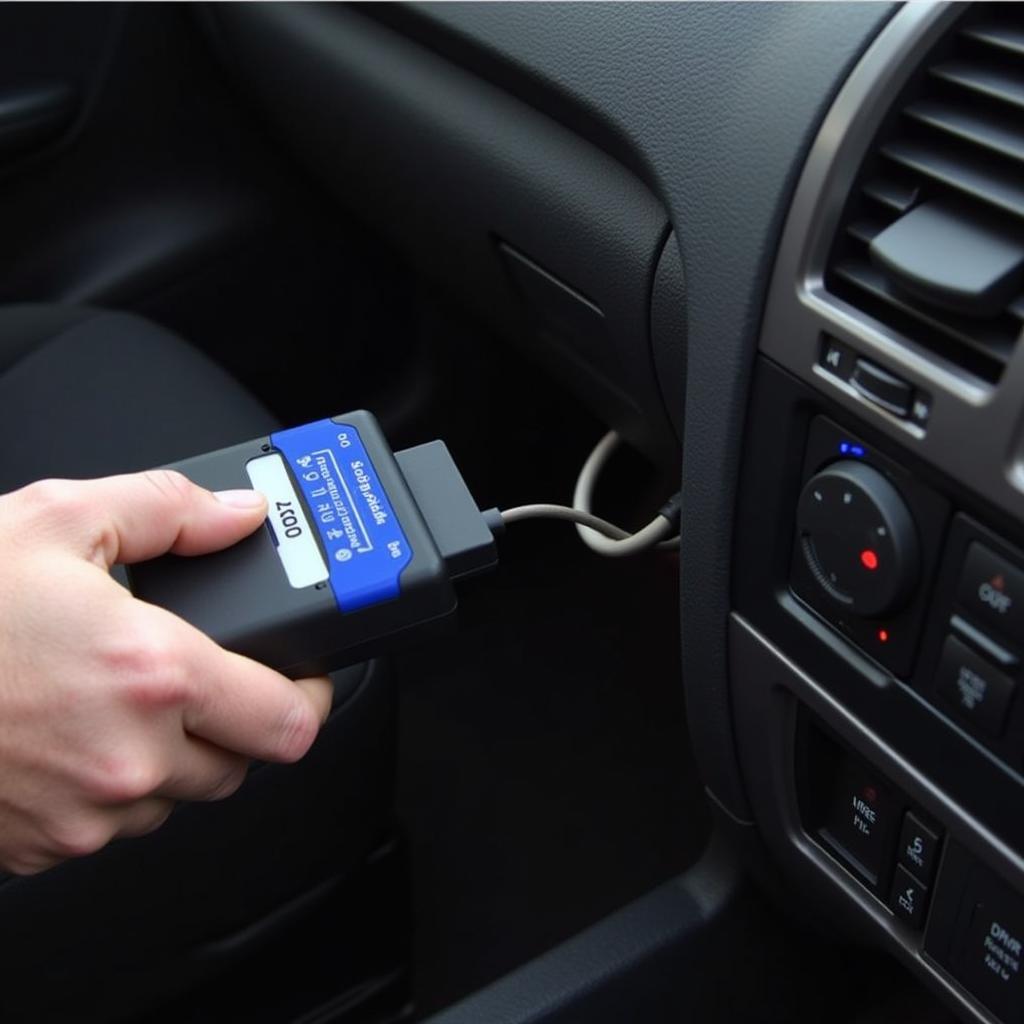 Connecting OBD2 Scanner to Car's Diagnostic Port
Connecting OBD2 Scanner to Car's Diagnostic Port
Interpreting the Codes
Once you have the codes, you need to interpret them. While some scanners provide a brief description of the code, using a reliable code lookup resource offers a more comprehensive understanding.
- Online databases: Numerous online resources offer detailed explanations of DTCs. Simply enter the code to access its meaning, possible causes, and common solutions.
- Repair manuals: These manuals provide in-depth information specific to your car model, including diagnostic procedures and repair instructions.
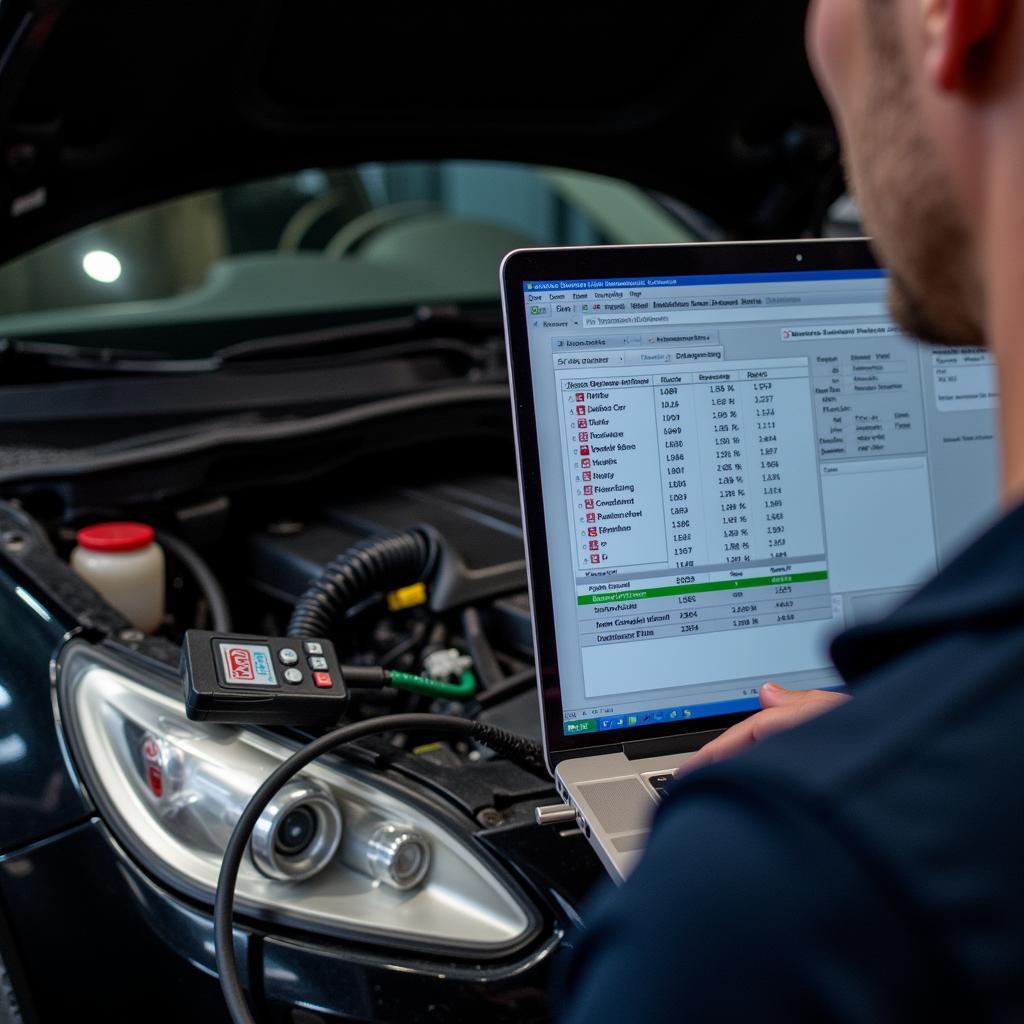 Mechanic Using Laptop for Car Diagnostics
Mechanic Using Laptop for Car Diagnostics
Common Car Scanner Codes and Their Meanings
Some common codes include:
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
Understanding these codes helps you pinpoint the problem area. For example, P0171 indicates an issue with the air-fuel mixture, while P0300 points to a problem with the ignition system or fuel delivery. The RAC car diagnostic scanner can provide descriptions of these common codes.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
While reading codes is essential, it’s often just the first step. Further diagnosis may involve checking sensors, testing components, and using specialized diagnostic tools. Tools like the Bluedriver Bluetooth Pro OBDII Scan Tool for iPhone & Android allow for more advanced diagnostics.
Similar to the Wsiiroon car wifi obd2 scanner, the Bluedriver provides live data streaming and other advanced features, allowing you to delve deeper into the issue.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Always clear the codes after repairs and retest to ensure the problem is resolved.
- Consider the context: Multiple codes might be related to a single underlying issue.
- Consult a qualified mechanic if you’re unsure how to proceed.
Conclusion
Knowing How To Read Car Scanner Codes is an invaluable skill. It empowers you to understand your vehicle’s health, make informed repair decisions, and potentially save money. While this guide provides a solid foundation, remember that proper diagnosis often involves further investigation. For assistance with your automotive diagnostic needs, connect with ScanToolUS at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1615 S Laramie Ave, Cicero, IL 60804, USA. Mastering how to read car scanner codes puts you in the driver’s seat when it comes to your vehicle’s maintenance.
Similar to a CDS scan tool, understanding the process can demystify car repairs. With this knowledge, you’re equipped to tackle automotive issues head-on.