In the realm of automotive repair, having a deep understanding of Diagnostic Tools And Techniques is crucial for efficiently identifying and rectifying vehicle issues. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a car enthusiast looking to delve into DIY repairs, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to tackle automotive problems head-on.
The Importance of Accurate Automotive Diagnosis
Before diving into the specifics of diagnostic tools and techniques, it’s essential to understand why accurate diagnosis is paramount. Just as a doctor relies on diagnostic tools to determine the root cause of an illness, automotive technicians depend on these tools to pinpoint the source of vehicle malfunctions.
Misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary repairs, wasted time and money, and even potential safety hazards. Imagine replacing a perfectly functional alternator based on a hunch when the actual culprit was a loose battery terminal!
 Loose battery terminal
Loose battery terminal
Effective diagnosis relies on a systematic approach, combining technical expertise with the proper use of diagnostic tools.
Essential Diagnostic Tools for Modern Vehicles
The automotive industry has witnessed a significant shift towards sophisticated electronics and computer-controlled systems. As a result, modern vehicles demand a new breed of diagnostic tools capable of communicating with these intricate networks. Let’s explore some of the indispensable tools found in any well-equipped automotive workshop:
1. OBD-II Scanners: Decoding the Language of Your Car
OBD-II scanners are arguably the most crucial tools in a modern mechanic’s arsenal. They serve as a direct line of communication with a vehicle’s onboard computer, retrieving Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that provide valuable insights into the nature and location of potential problems.
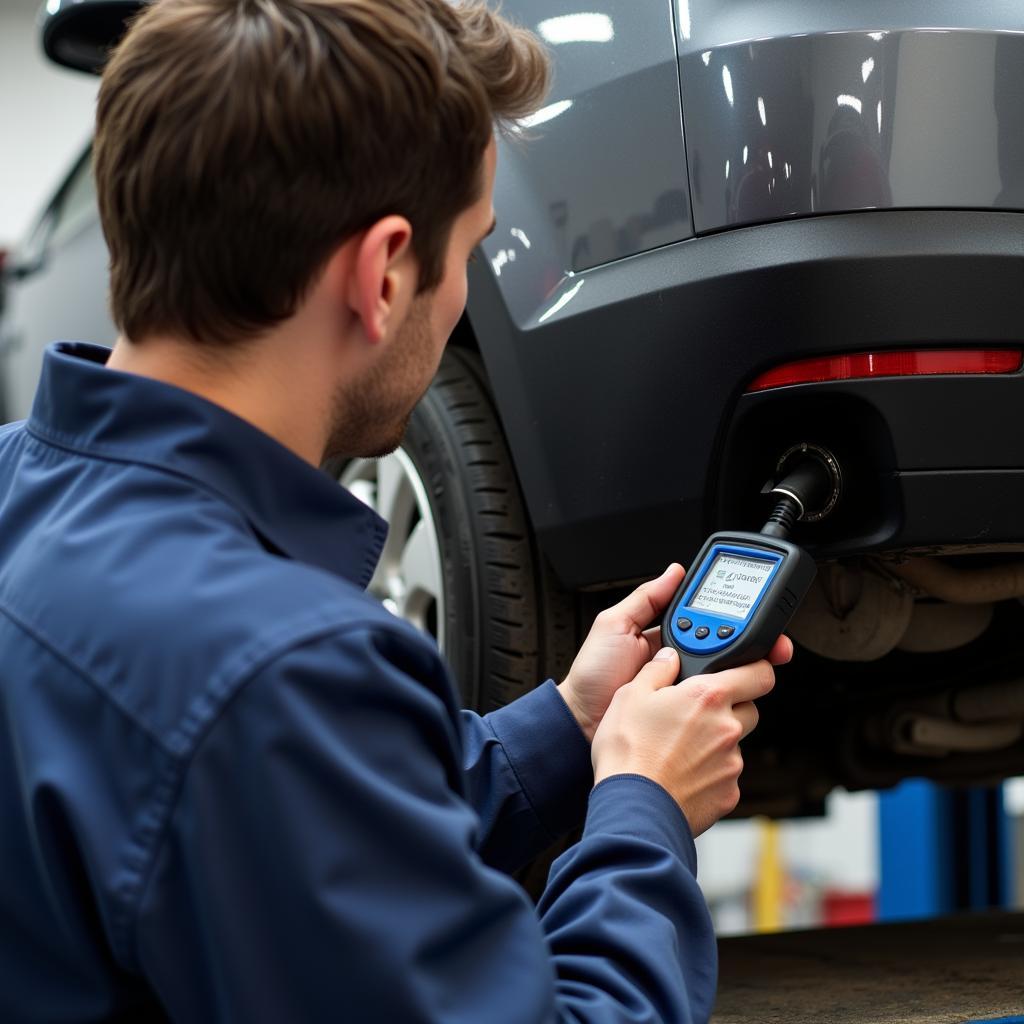 Mechanic using an OBD-II scanner
Mechanic using an OBD-II scanner
Beyond simply reading codes, advanced OBD-II scanners offer a plethora of features, including:
- Live Data Streaming: Monitor real-time sensor readings, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor voltage, to analyze system performance.
- Bi-directional Control: Interact with vehicle systems to actuate components like solenoids, relays, and actuators, aiding in component testing.
- ECU Coding and Programming: Modify vehicle settings, such as injector timing and idle speed, often requiring specialized software and knowledge.
2. Multimeters: The Cornerstone of Electrical Diagnosis
Multimeters are indispensable for diagnosing electrical issues, which are increasingly common in modern vehicles. These versatile tools measure voltage, current, resistance, and continuity, enabling technicians to:
- Test Battery Health: Determine the battery’s state of charge and cranking power.
- Diagnose Charging System Problems: Identify faulty alternators, voltage regulators, or wiring issues.
- Trace Electrical Faults: Locate shorts, opens, or high resistance areas in wiring harnesses.
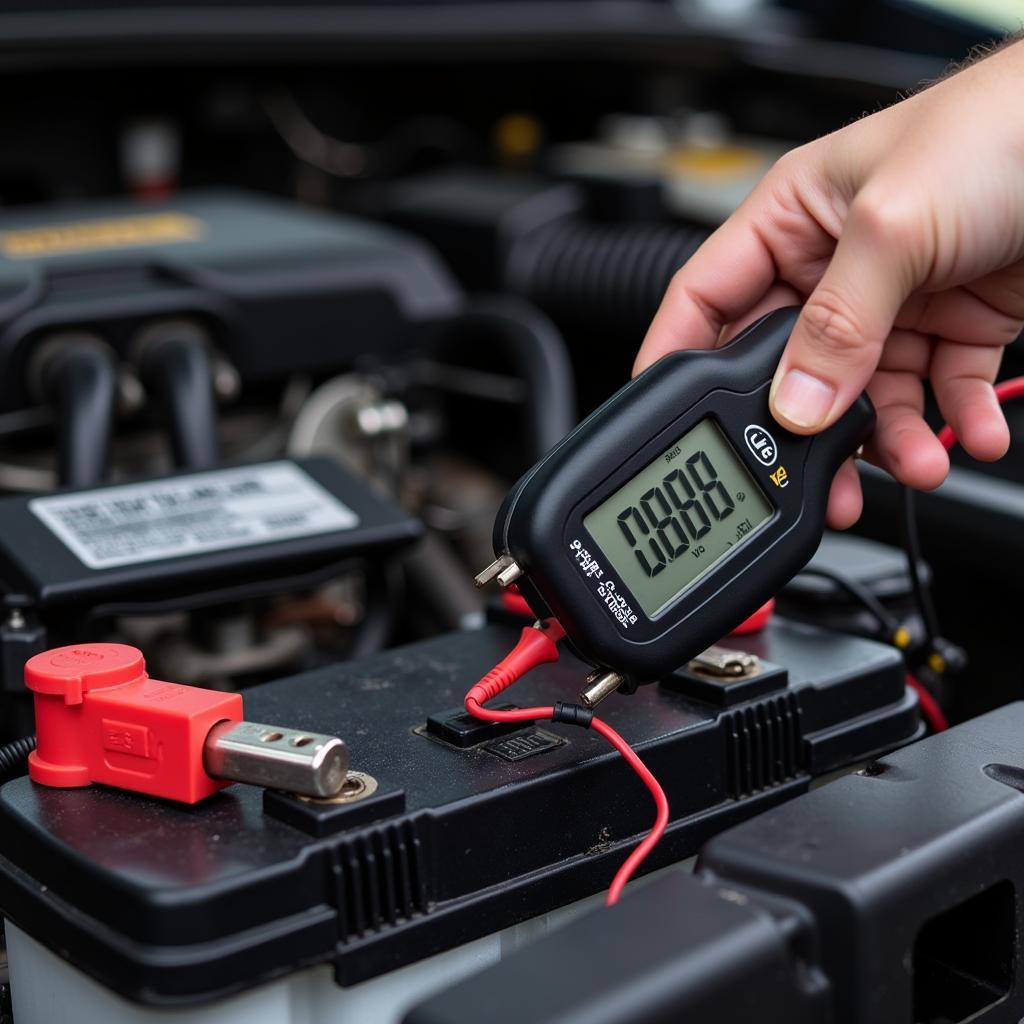 Multimeter measuring car battery voltage
Multimeter measuring car battery voltage
3. Oscilloscopes: Capturing Transient Signals
While multimeters excel at measuring steady-state values, oscilloscopes take automotive diagnosis to the next level by capturing and displaying rapidly changing signals over time. This capability proves invaluable when troubleshooting issues related to:
- Ignition Systems: Analyze spark plug firing patterns and identify misfires or weak sparks.
- Sensors: Evaluate the waveforms of various sensors, such as crankshaft position sensors and camshaft position sensors, to detect anomalies.
- Actuators: Observe the response time and performance of actuators, like fuel injectors and ignition coils.
4. Pressure Gauges: Monitoring Fluid Systems
Many critical vehicle systems rely on pressurized fluids for proper operation, making pressure gauges crucial for:
- Fuel System Diagnosis: Test fuel pressure and diagnose problems with the fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, or fuel lines.
- Cooling System Analysis: Monitor coolant pressure to detect leaks, head gasket issues, or a malfunctioning thermostat.
- Transmission Fluid Pressure: Ensure proper transmission fluid pressure, which is vital for smooth shifting and overall transmission health.
Mastering Diagnostic Techniques
Possessing the right tools is only half the battle. Equally crucial are the techniques employed to interpret the data collected and arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
1. Visual Inspection: The First Line of Defense
Before reaching for any sophisticated tools, a thorough visual inspection is paramount. This seemingly simple step can often reveal telltale signs of trouble:
- Fluid Leaks: Check for puddles of fluid under the vehicle, which could indicate problems with the engine oil, coolant, transmission fluid, or brake fluid.
- Damaged Components: Examine belts, hoses, wiring, and components for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion.
- Loose Connections: Verify that battery terminals, wiring harnesses, and sensor connections are secure.
2. DTC Analysis: Deciphering the Codes
When an OBD-II scanner retrieves DTCs, it’s crucial to understand their meaning and avoid jumping to conclusions.
- Identify the System: DTCs typically consist of a letter and four digits. The letter indicates the system involved, such as “P” for powertrain or “B” for body.
- Research the Code: Consult reliable sources, like factory service manuals or reputable online databases, to understand the specific meaning of each code.
- Consider Potential Causes: DTCs often have multiple potential causes. Further investigation using live data, component testing, or other diagnostic procedures is usually necessary.
[using microsoft debug diagnostic tool](https://scantoolus.com/using-microsoft-debug-diagnostic tool/)
3. Systematic Troubleshooting: A Step-by-Step Approach
When faced with complex or intermittent issues, a systematic approach is vital to avoid getting lost in a maze of possibilities.
- Gather Information: Obtain a detailed history of the problem from the vehicle owner, including the symptoms, when they occur, and any recent repairs.
- Verify the Issue: If possible, replicate the problem to confirm the symptoms and narrow down the potential causes.
- Test Components: Utilize appropriate tools and procedures to test suspected components, starting with the most likely culprits based on the symptoms and DTCs.
- Re-evaluate and Refine: As you gather more information, re-evaluate your diagnosis and adjust your approach if necessary.
4. Seeking Expert Assistance
While DIY repairs can be rewarding, certain issues demand the expertise of trained professionals. Don’t hesitate to consult with a qualified automotive technician if you encounter:
- Complex Electronic Issues: Modern vehicles are heavily reliant on sophisticated electronic systems that require specialized knowledge and equipment.
- Safety-Critical Repairs: Brakes, steering, and airbag systems are crucial for vehicle safety and should always be handled by trained professionals.
- Lack of Proper Tools or Expertise: Attempting repairs without the right tools or knowledge can lead to further damage or safety hazards.
“In today’s world of intricate automotive technology, having a solid grasp of both the tools and the techniques for accurate diagnosis is paramount,” says John Smith, a seasoned automotive engineer with over 20 years of experience. “It’s not just about fixing cars anymore; it’s about understanding the language they speak.”
Conclusion
Mastering automotive diagnostic tools and techniques is an ongoing journey that requires a combination of theoretical knowledge, practical experience, and a passion for staying abreast of the latest advancements in automotive technology. By embracing a systematic approach, utilizing the right tools, and seeking expert assistance when needed, you can confidently tackle even the most challenging automotive issues, ensuring vehicles run smoothly and safely for miles to come.
Need help with car diagnostics? Contact ScanToolUS at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1615 S Laramie Ave, Cicero, IL 60804, USA. Our experts are here to assist you.
FAQs
1. What should I do if my check engine light comes on?
When your check engine light illuminates, it’s crucial to get your vehicle diagnosed as soon as possible. Connect an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), then consult a reliable source to understand their meaning.
2. Can I use any OBD-II scanner on my car?
While most OBD-II scanners can read basic codes, certain vehicles may require specialized scanners for accessing manufacturer-specific systems or advanced functions.
3. How often should I have my car’s battery tested?
It’s generally recommended to have your car’s battery tested at least once a year, especially before the winter months when batteries are subjected to increased stress.
4. Is it worth investing in professional-grade diagnostic tools for DIY repairs?
The value of investing in professional-grade tools depends on your level of expertise and the complexity of repairs you plan to undertake. Basic tools might suffice for simple tasks, while complex issues might require specialized equipment.
5. What are some common signs of a failing alternator?
Dimming headlights, flickering dashboard lights, and a whining sound from the engine bay are common indicators of a failing alternator. You can use a multimeter to check the battery’s voltage while the engine is running to confirm alternator function.