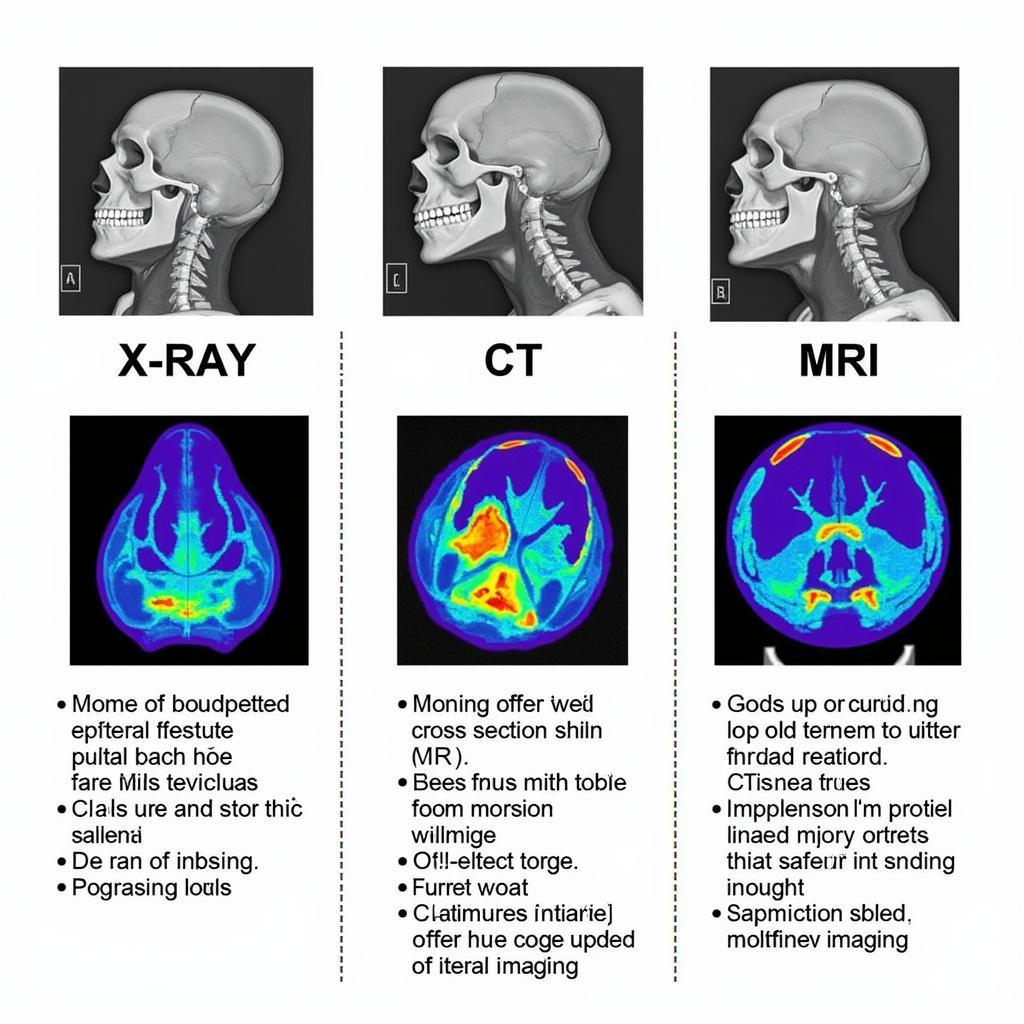
The correlation between diagnostic tool readings and a patient’s ability to perform Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) is crucial in understanding and managing dyspnea. Dyspnea, often described as shortness of breath, can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, limiting their ability to perform even the simplest tasks. By utilizing diagnostic tools effectively, healthcare professionals can accurately classify the severity of dyspnea and tailor treatment plans to improve a patient’s ability to perform ADLs.
The Importance of Accurate Dyspnea Classification
Accurately classifying the severity of dyspnea is the first step towards effective management. Various methods are used to assess dyspnea, including:
- Visual Analog Scales (VAS): These scales allow patients to rate their perceived breathlessness on a scale, typically from 0 to 10.
- Modified Borg Scale: This scale uses a numerical rating system (0-10) with corresponding descriptive terms to assess breathlessness during activity.
- Baseline Dyspnea Index (BDI): This questionnaire-based tool assesses the functional impact of dyspnea by asking patients about their breathing difficulty during specific activities.
 Dyspnea Assessment Tools
Dyspnea Assessment Tools
These tools, along with a thorough medical history and physical examination, help healthcare providers determine the underlying cause of dyspnea and its impact on a patient’s daily life.
Diagnostic Tools for Identifying the Cause of Dyspnea
Identifying the root cause of dyspnea is essential for effective treatment. Several diagnostic tools play a vital role in this process:
- Spirometry: This test measures lung function, including the amount of air a person can inhale and exhale, as well as the speed of airflow. It helps diagnose conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pulmonary fibrosis.
- Pulse Oximetry: This non-invasive test measures the oxygen saturation in the blood, providing insights into how well the lungs are transferring oxygen to the rest of the body.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the heart’s electrical activity and can help diagnose heart conditions that may cause dyspnea, such as arrhythmias or heart failure.
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray provides images of the lungs, heart, and surrounding structures, aiding in the identification of conditions like pneumonia, lung cancer, or heart enlargement.
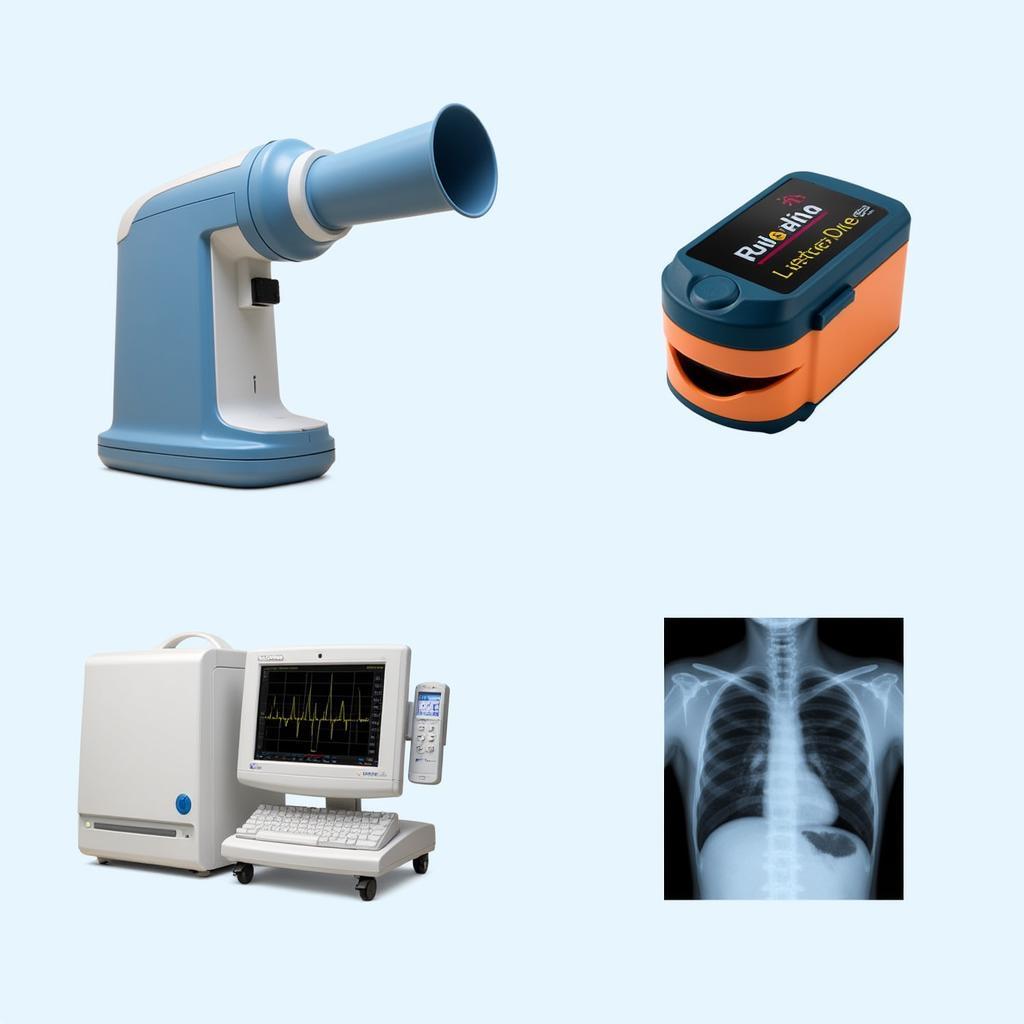 Diagnostic Tools for Dyspnea
Diagnostic Tools for Dyspnea
Correlating Diagnostic Findings with ADL Performance
Once the severity of dyspnea is classified and the underlying cause is identified, healthcare providers can focus on correlating these findings with a patient’s ability to perform ADLs. This involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s functional limitations:
- Basic ADLs: These are essential activities like bathing, dressing, eating, toileting, and mobility.
- Instrumental ADLs (IADLs): These are more complex activities necessary for independent living, such as cooking, managing finances, shopping, and transportation.
The correlation between diagnostic findings and ADL performance helps healthcare providers develop a targeted treatment plan.
“For instance, a patient diagnosed with moderate COPD based on spirometry results may experience shortness of breath when walking short distances or climbing stairs. This information helps us tailor interventions, such as pulmonary rehabilitation or supplemental oxygen, to improve their ability to perform these specific activities,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a respiratory therapist at a leading pulmonary rehabilitation center.
Treatment Strategies to Improve ADL Performance
Treatment for dyspnea varies depending on the underlying cause. However, some common treatment strategies include:
- Medications: Bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and oxygen therapy are frequently used to manage dyspnea in conditions like asthma and COPD.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: This comprehensive program combines exercise, education, and support to improve lung function and reduce breathlessness.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Quitting smoking, avoiding environmental triggers, and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial for improving dyspnea.
- Energy Conservation Techniques: Patients can learn techniques to conserve energy and minimize breathlessness during daily activities.
 Treatment Options for Dyspnea
Treatment Options for Dyspnea
The Role of Technology in Managing Dyspnea
Technological advancements have significantly impacted the management of dyspnea.
- Telehealth: Remote patient monitoring allows healthcare providers to track patients’ symptoms, oxygen levels, and medication adherence, enabling timely interventions.
- Wearable Sensors: Wearable devices can monitor heart rate, respiratory rate, and activity levels, providing valuable data to assess dyspnea and track progress.
- Mobile Health Applications: These apps can provide patients with education, self-management tools, and access to support communities.
Conclusion
Understanding the correlation between diagnostic tool findings and a patient’s ability to perform ADLs is crucial for the effective management of dyspnea. By utilizing a combination of accurate classification, targeted treatments, and technological advancements, healthcare providers can empower patients to manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and regain their independence in performing daily activities.
If you or a loved one is struggling with dyspnea, contact ScanToolUS at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1615 S Laramie Ave, Cicero, IL 60804, USA. Our team of experts can provide guidance and support in managing this condition.