A bad front oxygen (O2) sensor can cause all sorts of trouble with your car’s performance and fuel efficiency. Diagnosing a bad front o2 sensor with a scan tool is the first step towards fixing the problem and getting your car running smoothly again. This article will guide you through the process, from understanding the role of the O2 sensor to interpreting scan tool data and ultimately replacing the faulty sensor.
Understanding the Front O2 Sensor’s Role
The front O2 sensor, also known as the upstream O2 sensor, is a critical component of your vehicle’s emissions control system. It constantly monitors the oxygen content in the exhaust gases leaving the engine and relays this information to the engine control unit (ECU). This data allows the ECU to adjust the air-fuel mixture, ensuring optimal combustion, fuel efficiency, and minimal emissions.
Symptoms of a Bad Front O2 Sensor
A failing front o2 sensor can manifest in various ways. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and preventing further damage. Common signs include decreased fuel economy, rough idling, hesitation or stumbling during acceleration, and even a check engine light. You might also notice a sulfur-like smell from your exhaust.
Diagnosing a Bad Front O2 Sensor with a Scan Tool
While the check engine light is a good indicator, it doesn’t pinpoint the exact problem. This is where a scan tool becomes invaluable. Connecting a scan tool to your car’s OBD-II port allows you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and live sensor data. Specific DTCs related to a bad front o2 sensor include P0130 (O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction Bank 1 Sensor 1), P0131 (O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage Bank 1 Sensor 1), and P0132 (O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage Bank 1 Sensor 1).
Besides DTCs, observing live data from the front o2 sensor provides valuable insights. A healthy sensor’s voltage should fluctuate rapidly between 0.1 and 0.9 volts, indicating it’s actively monitoring oxygen levels. A sluggish or stuck voltage reading suggests a faulty sensor.
What does a bad front O2 sensor reading look like on a scan tool?
A bad front O2 sensor reading on a scan tool can manifest as a consistently low or high voltage, a lack of fluctuation, or a slow response to changes in engine operation.
Replacing a Bad Front O2 Sensor
Once you’ve confirmed a bad front o2 sensor with your scan tool, replacement is the next step. Locate the sensor on your exhaust manifold or exhaust pipe. Before removal, spray penetrating oil around the sensor threads to prevent seizing. Disconnect the electrical connector and carefully unscrew the sensor using an O2 sensor socket. Install the new sensor, tightening it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Can I drive with a bad front O2 sensor?
While you technically can drive with a bad front O2 sensor, it’s not recommended. It can lead to decreased fuel efficiency, potential damage to your catalytic converter, and failed emissions tests.
“Ignoring a bad O2 sensor is like ignoring a leaky faucet,” says automotive expert, David Miller. “It might seem small, but it can lead to bigger problems down the road.”
Further Troubleshooting with a Scan Tool
Even after replacing the sensor, it’s essential to clear the DTCs with your scan tool and monitor the live data again. This ensures the new sensor is functioning correctly and the issue is resolved. If the problem persists, further diagnostics might be needed to rule out other potential issues.
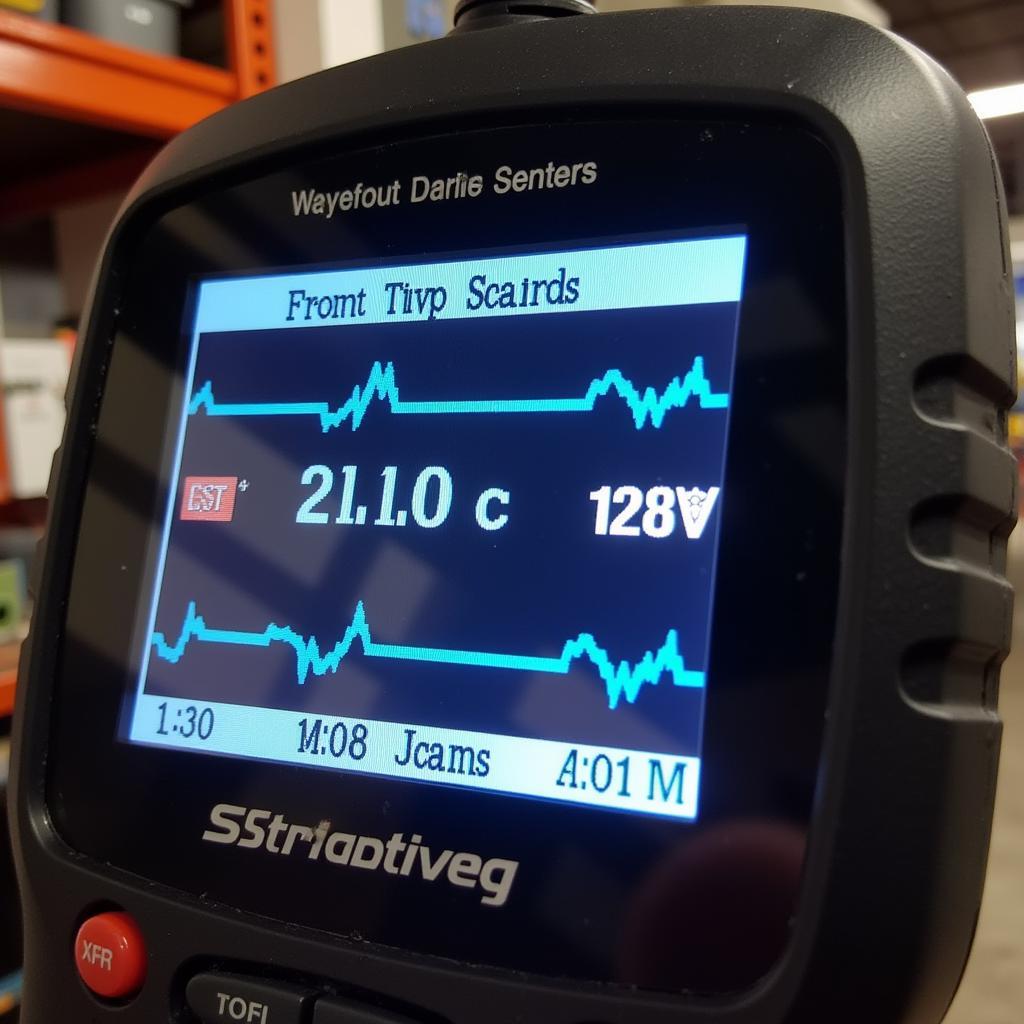 Checking New O2 Sensor Readings with a Scan Tool
Checking New O2 Sensor Readings with a Scan Tool
How do I reset the check engine light after replacing the O2 sensor?
Most scan tools have a function to clear DTCs, effectively resetting the check engine light. Alternatively, disconnecting the battery for a short period can also reset it, although this might also reset other vehicle settings.
“Using a scan tool for diagnostics empowers car owners to understand their vehicles better,” adds Sarah Johnson, a seasoned automotive technician. “It’s a valuable investment for any DIY enthusiast.”
 Front Oxygen Sensor Location on the Exhaust Manifold
Front Oxygen Sensor Location on the Exhaust Manifold
In conclusion, diagnosing a bad front o2 sensor with a scan tool is a straightforward process that can save you money and headaches. By understanding the sensor’s role, recognizing the symptoms, and utilizing a scan tool effectively, you can pinpoint the issue, replace the faulty sensor, and get your car back in top shape. For further assistance or questions about scan tools, feel free to contact us at ScanToolUS. Our phone number is +1 (641) 206-8880 and our office is located at 1615 S Laramie Ave, Cicero, IL 60804, USA.
FAQ
- What is the lifespan of a front O2 sensor? Typically, front O2 sensors last between 60,000 and 90,000 miles.
- How much does it cost to replace a front O2 sensor? The cost varies depending on the make and model of your car but generally ranges from $100 to $300, including parts and labor.
- Can I replace the front O2 sensor myself? Yes, replacing an O2 sensor is a relatively simple DIY task for those with basic mechanical skills.
- What tools do I need to replace a front O2 sensor? You’ll primarily need an O2 sensor socket, penetrating oil, and potentially a wrench set.
- Why is my check engine light still on after replacing the O2 sensor? This could indicate another issue, or the DTCs haven’t been cleared. Try clearing the codes with a scan tool.
- How do I choose the right replacement O2 sensor? Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or use an online parts finder to ensure you purchase the correct sensor for your specific make and model.
- What are the symptoms of a bad rear O2 sensor? Similar to the front sensor, a bad rear O2 sensor can trigger the check engine light and might affect fuel efficiency, though it usually won’t cause drivability issues like rough idling.

