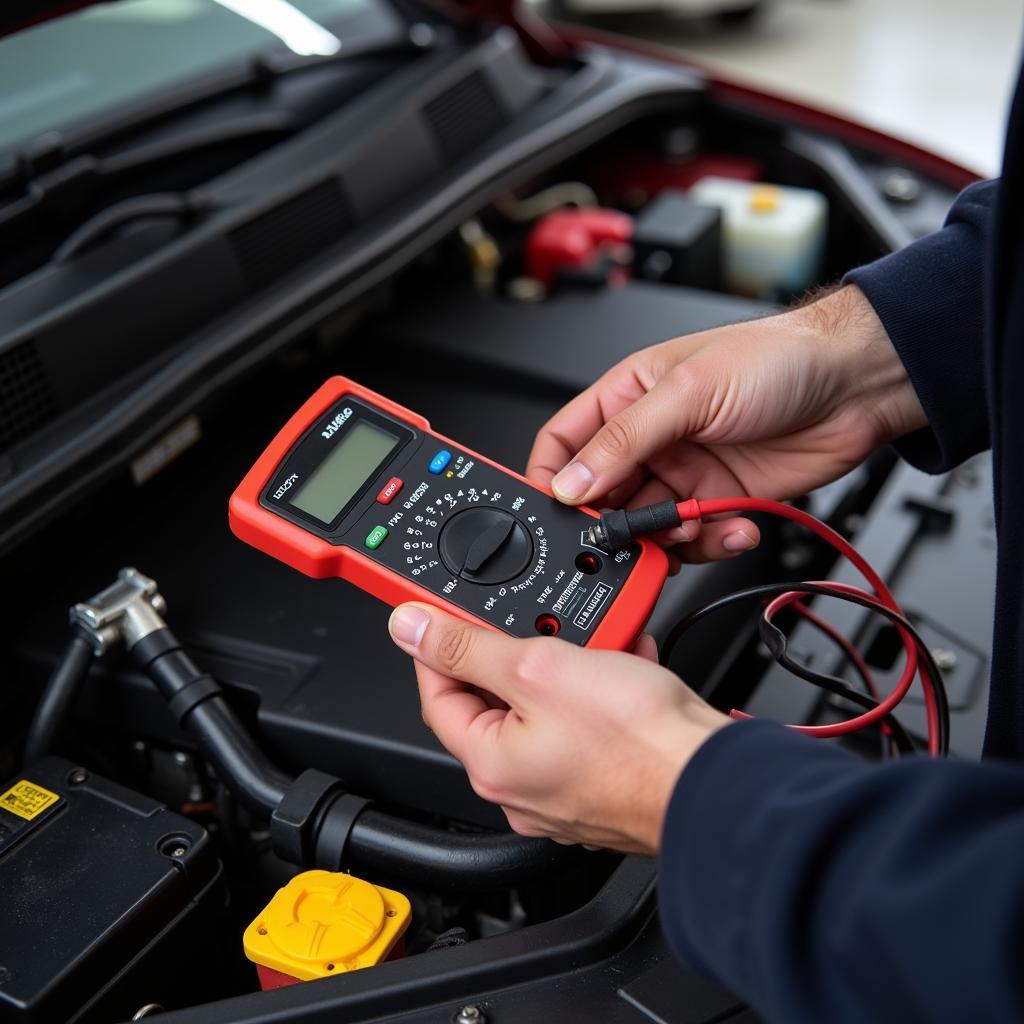
An Auto Obd2 Diagnostic Tool is an essential piece of equipment for any car owner, mechanic, or DIY enthusiast. It allows you to communicate with your car’s computer, read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and troubleshoot issues effectively. Whether you’re experiencing engine problems, transmission hiccups, or pesky warning lights, this tool can help you get to the root of the problem.
What is an Auto OBD2 Diagnostic Tool and How Does It Work?
OBD2 stands for On-Board Diagnostics, generation 2. This standardized system, mandatory in all vehicles manufactured after 1996 (US) and 2001 (EU), provides valuable insights into the various systems within your car. An OBD2 diagnostic tool acts as the bridge between your car’s computer and you. It connects to the OBD2 port, usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, and retrieves data from the car’s computer.
 Car OBD2 Port Location
Car OBD2 Port Location
Benefits of Owning an Auto OBD2 Diagnostic Tool
Investing in an auto OBD2 diagnostic tool offers numerous benefits:
- Save Money: Diagnose car problems yourself and potentially avoid costly mechanic fees.
- Early Detection: Identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
- Increased Knowledge: Gain a deeper understanding of your car’s health and performance.
- Peace of Mind: Feel confident and empowered to tackle car issues head-on.
Types of Auto OBD2 Diagnostic Tools
Several types of OBD2 diagnostic tools are available, each with varying features and price points:
- Basic Code Readers: These affordable tools retrieve and display DTCs, providing a starting point for diagnosis.
- Bluetooth or Wi-Fi Adapters: These compact devices connect to your smartphone or tablet, allowing you to use diagnostic apps with advanced features.
- elm327 bluetooth obd2 v1 5 car diagnostic interface tool is an excellent example of this type of tool, providing a wireless and convenient way to diagnose your car using your smartphone.
- Professional-Grade Scan Tools: Used by mechanics and professionals, these tools offer comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including live data streaming, bi-directional control, and advanced programming functions.
- To explore the best options for professional use, you can find a list of the [best dealer level diagnostic tools](https://scantoolus.com/best-dealer-level-diagnostic tools/) on our website.
 Different Types of OBD2 Scanners
Different Types of OBD2 Scanners
Choosing the Right Auto OBD2 Diagnostic Tool
Consider the following factors when selecting an auto OBD2 diagnostic tool:
- Your Budget: Determine how much you are willing to spend on the tool.
- Your Skill Level: Choose a tool that matches your technical expertise.
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the tool supports your car’s make, model, and year.
- Desired Features: Identify the features that are important to you, such as live data, ABS, airbag, or transmission diagnostics.
- For those interested in more advanced diagnostics, an er diagnostic tool offers specialized functionalities for enhanced troubleshooting.
Using an Auto OBD2 Diagnostic Tool
Using an auto OBD2 diagnostic tool is relatively straightforward:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Refer to your car’s manual if needed.
- Connect the Tool: Plug the tool into the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the key to the “on” position but don’t start the engine.
- Read Codes: Follow the tool’s instructions to read and record any DTCs.
- Research Codes: Use online resources or repair manuals to understand the meaning of the codes.
- Clear Codes: After addressing the issues, use the tool to clear the codes and verify the repairs.
Important Note: While an OBD2 diagnostic tool is a powerful tool, it’s crucial to remember that it only provides clues. Proper diagnosis often requires further investigation, mechanical knowledge, and, in some cases, the expertise of a qualified mechanic.
Common Auto OBD2 Diagnostic Tool Error Codes
Here are a few common OBD2 error codes and their potential meanings:
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) – This code often indicates a failing catalytic converter.
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected – This code suggests engine misfires, which could be due to spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel system issues.
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1) – This code indicates that the engine is running lean, meaning there’s too much air or not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture.
For a comprehensive understanding of diagnostic tools and techniques, you can find valuable information on our website.
“Using an OBD2 tool is like having a window into your car’s brain,” says John Smith, Senior Automotive Engineer at ScanToolUS. “It empowers you to make informed decisions about your car’s maintenance and repairs.”
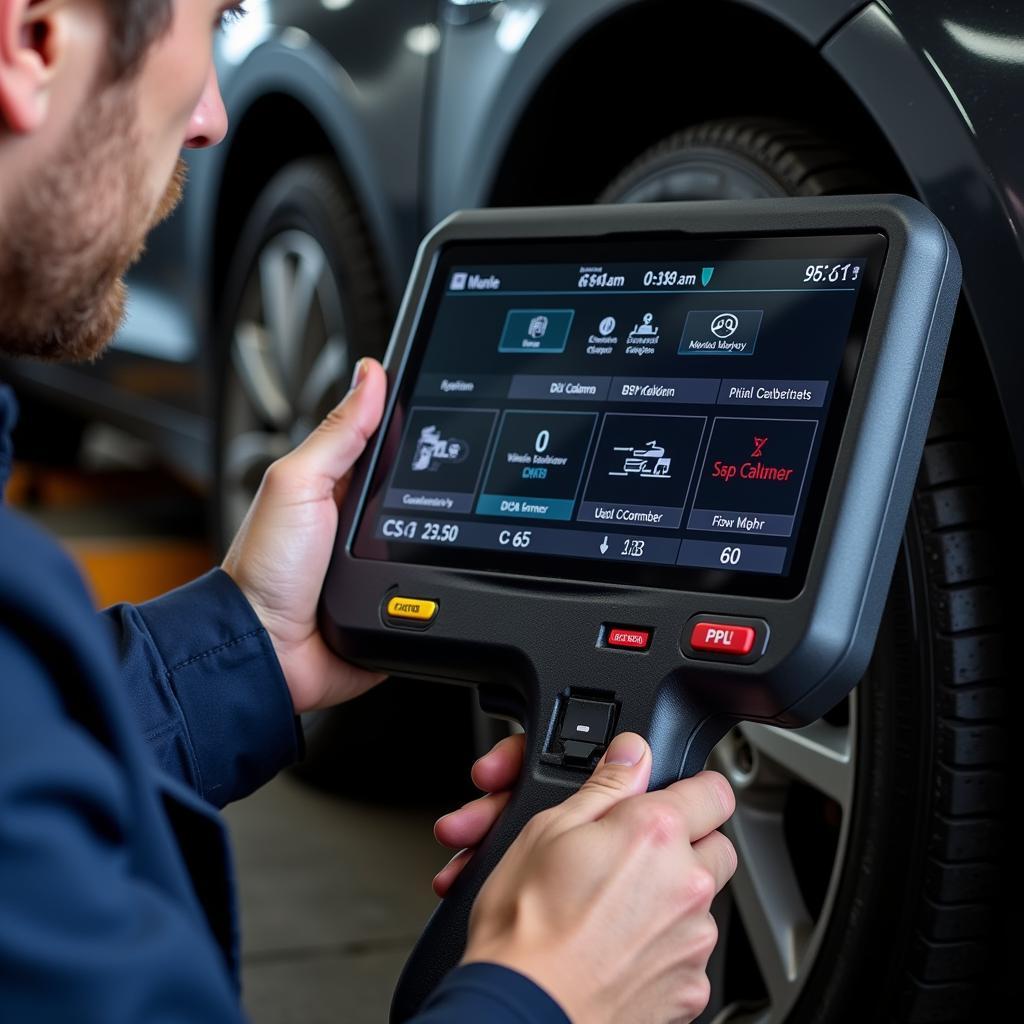 Mechanic Using an OBD2 Scanner
Mechanic Using an OBD2 Scanner
Maintaining Your Auto OBD2 Diagnostic Tool
To ensure your OBD2 diagnostic tool continues to function correctly, follow these tips:
- Store it Properly: Keep the tool in a clean, dry place when not in use.
- Update Software: Regularly check for and install software updates to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping or mishandling the tool.
Conclusion
An auto OBD2 diagnostic tool is an indispensable tool for anyone who owns, maintains, or repairs cars. It provides valuable insights into your car’s health, enabling you to diagnose problems accurately and potentially save time and money. With the right tool and a bit of knowledge, you can become a more informed and confident car owner.
For expert advice and assistance in choosing the right auto OBD2 diagnostic tool for your needs, contact ScanToolUS at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1615 S Laramie Ave, Cicero, IL 60804, USA. We’re here to help you keep your car running smoothly.