Understanding how to read diagnostic tools is crucial for any car owner, mechanic, or automotive technician. These tools provide a window into the inner workings of a vehicle, revealing hidden problems and helping pinpoint the source of malfunctions. Mastering this skill can save you time, money, and frustration in the long run.
Similar to a professional pc hardware diagnostic tools, automotive diagnostic tools have evolved significantly from simple code readers to sophisticated software suites capable of analyzing complex systems. This article will guide you through the essential steps of interpreting the data from these tools, empowering you to diagnose and fix car problems effectively.
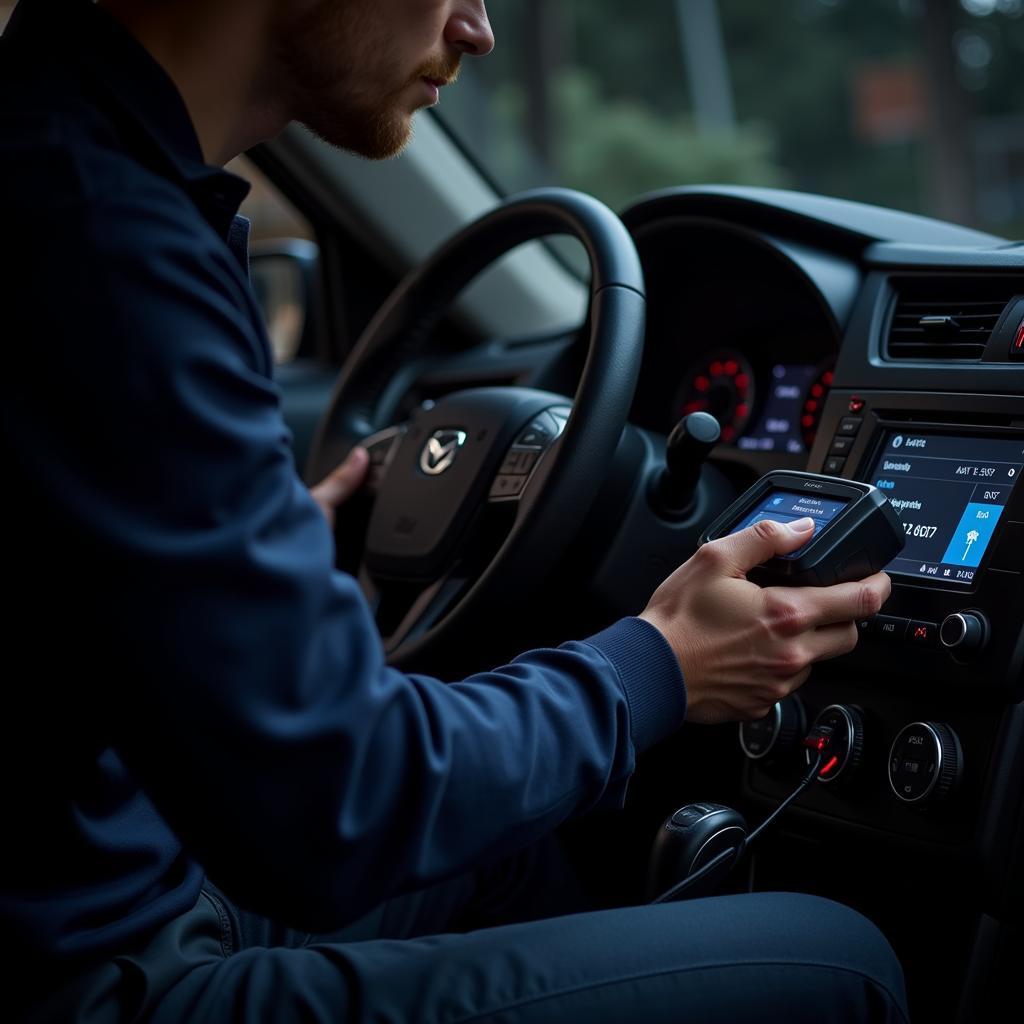 Mechanic Reading OBD-II Scanner in a Car
Mechanic Reading OBD-II Scanner in a Car
Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
The foundation of automotive diagnostics lies in understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These codes, standardized by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), are five-character alphanumeric sequences that represent specific malfunctions within the vehicle’s systems. The first character indicates the system affected (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network). The remaining characters pinpoint the specific nature of the problem. For instance, P0301 indicates a misfire in cylinder 1. Accurate interpretation of these codes is the first step towards a correct diagnosis.
Using an OBD-II Scanner
The OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is the most common diagnostic tool. It connects to the vehicle’s OBD-II port, usually located under the dashboard. Once connected, the scanner retrieves DTCs stored in the vehicle’s computer. Many scanners also display live data from various sensors, providing real-time insights into the vehicle’s performance. How To Read Diagnostic Tools For Automobiles often starts with understanding the OBD-II scanner and its functions.
What are the common uses of an OBD-II scanner? OBD-II scanners are used to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes, monitor live sensor data, and perform various diagnostic tests depending on the scanner’s capabilities.
Beyond the OBD-II Scanner: Advanced Diagnostic Tools
While the OBD-II scanner is invaluable, more advanced diagnostic tools offer deeper insights for complex issues. These tools, often software-based, can access manufacturer-specific data, perform advanced diagnostic tests, and even program certain vehicle modules. They allow for bi-directional communication with the vehicle’s systems, enabling technicians to activate components, such as actuators and relays, for testing purposes. An obd ii auto code scanner automotive diagnostic scan tool is a good starting point for many, but these advanced tools offer more functionality.
Why are advanced diagnostic tools necessary? Advanced diagnostic tools are crucial for diagnosing complex issues that basic OBD-II scanners can’t handle. They provide access to manufacturer-specific data and allow for more in-depth analysis.
Interpreting Live Data
Live data, displayed by many diagnostic tools, provides real-time information from various sensors throughout the vehicle. This data can be invaluable in diagnosing intermittent problems or verifying repairs. By observing changes in sensor readings under different operating conditions, you can pinpoint the source of a malfunction. For example, monitoring oxygen sensor readings while accelerating can reveal a faulty sensor or a vacuum leak.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
One common mistake is relying solely on DTCs without considering other factors. DTCs provide clues, but they don’t always pinpoint the exact cause. It’s crucial to combine DTC information with visual inspections, live data analysis, and other diagnostic tests to reach an accurate conclusion.
“Never jump to conclusions based solely on a DTC,” advises John Smith, Senior Automotive Engineer at AutoTech Solutions. “A thorough diagnostic process involves multiple steps and a holistic understanding of the vehicle’s systems.”
obd ii auto code scanner automotive diagnostic scan tool
What are some common misconceptions about diagnostic tools? One common misconception is that diagnostic tools can magically fix problems. They are simply tools to help pinpoint the source of the issue. The actual repair still requires mechanical expertise.
Keeping Up with Technology
Automotive technology is constantly evolving. New systems and protocols emerge regularly, requiring continuous learning and adaptation. Staying updated with the latest diagnostic tools and software is essential for effective troubleshooting.
“The automotive industry is rapidly changing,” notes Jane Doe, Lead Technician at Advanced Auto Repair. “Continuous learning is no longer optional; it’s a necessity for staying competitive and providing quality service.”
diagnostics tools visual studio 2015
How can I stay updated with the latest diagnostic tools and technology? Joining professional organizations, attending training workshops, and subscribing to automotive publications are excellent ways to stay up-to-date.
diagnostic tools for computer hardware
Conclusion
Learning how to read diagnostic tools for automobiles is a crucial skill for anyone involved in vehicle maintenance and repair. By understanding DTCs, utilizing OBD-II scanners effectively, and interpreting live data, you can unlock the secrets hidden within your car’s systems. Remember, these tools are powerful aids in the diagnostic process, but they are not a substitute for thorough inspection and critical thinking. For any questions or assistance with your diagnostic needs, feel free to contact us at ScanToolUS. Our team of experts is ready to help. You can reach us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1615 S Laramie Ave, Cicero, IL 60804, USA.