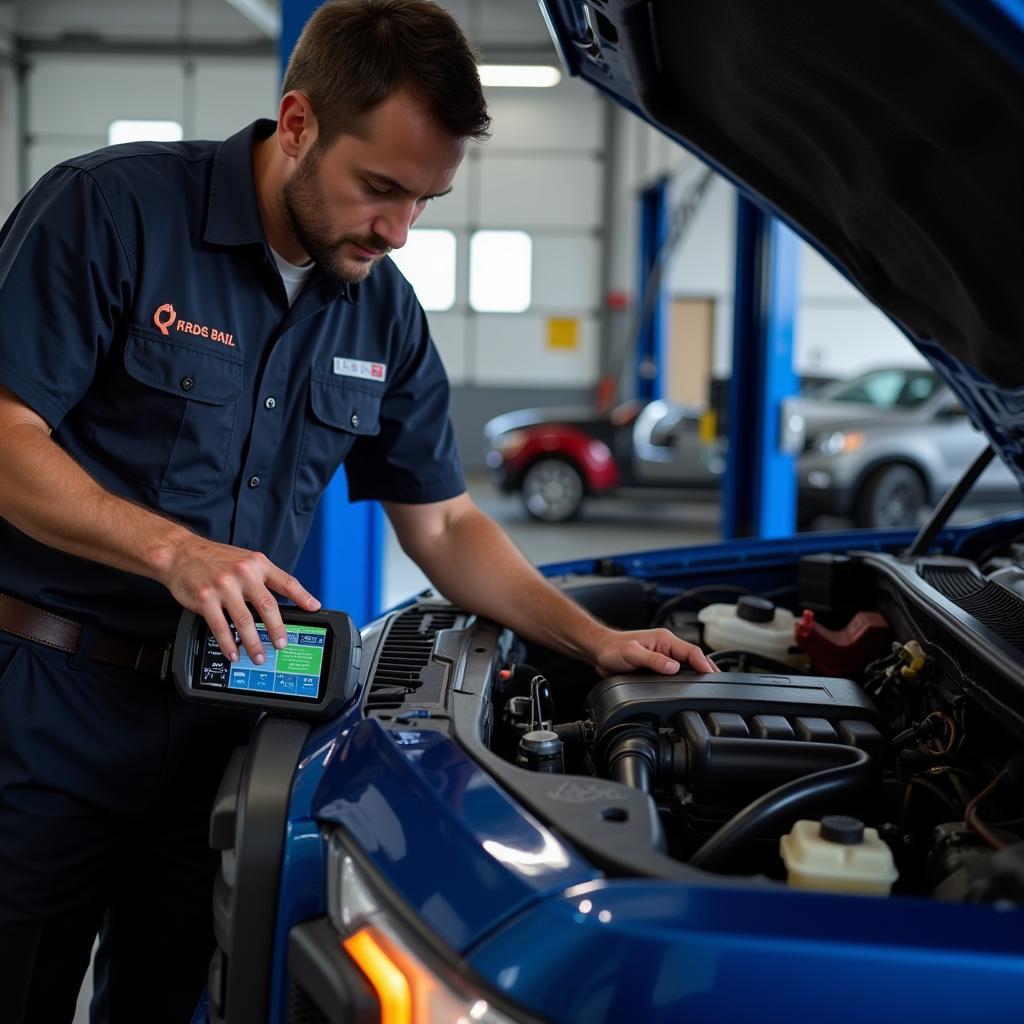
Classroom diagnostic tools are essential for modern automotive technicians. Understanding how to extract test results and interpret them is crucial for accurate diagnosis and efficient repair. This guide provides comprehensive instructions on using these tools effectively, focusing on test extract procedures within a classroom setting.
Understanding the Importance of Classroom Diagnostic Tools
Automotive technology is constantly evolving, with vehicles becoming increasingly complex. This necessitates the use of sophisticated diagnostic tools, even within a classroom environment. These tools allow students and instructors to simulate real-world scenarios and gain practical experience in diagnosing and troubleshooting automotive issues. Proper use of these tools, particularly understanding how to extract test data, is fundamental to mastering automotive diagnostics.
Classroom Diagnostic Tools Test Extract Instructions: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here’s a detailed guide to extracting test results from classroom diagnostic tools:
-
Connect the Tool: Ensure the diagnostic tool is correctly connected to the vehicle’s OBD-II port. Verify the connection is secure and the vehicle’s ignition is switched to the “on” position.
-
Power On the Tool: Turn on the diagnostic tool and allow it to initialize. This may involve a self-test or firmware update.
-
Vehicle Identification: Select the correct vehicle make, model, and year within the diagnostic tool’s software. Accurate vehicle identification is crucial for retrieving the correct diagnostic information.
-
Select the Appropriate Test: Choose the specific test you wish to perform based on the suspected issue. This could include reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitoring live data streams, or performing actuator tests.
-
Run the Test: Initiate the chosen test and allow the diagnostic tool to gather the necessary data. Observe any prompts or instructions displayed on the tool’s screen.
-
Extract the Test Results: Once the test is complete, navigate to the “data logging” or “test results” section within the tool’s software. This is where you’ll find the extracted data.
-
Saving and Interpreting Data: Save the extracted test results to a USB drive or the tool’s internal memory. This data can then be analyzed to pinpoint the root cause of the automotive problem.
Different Types of Classroom Diagnostic Tools and Their Extraction Methods
Various diagnostic tools are used in automotive classrooms, each with its own extraction method. Some common types include:
Code Readers:
These basic tools primarily read and clear DTCs. Extracting codes usually involves noting them down manually or using a simple print function.
Scan Tools:
Scan tools offer more advanced functionalities, including live data streaming and actuator tests. Test data can often be saved to a file or printed.
Oscilloscopes:
Oscilloscopes allow technicians to visualize electrical signals. Extracting data typically involves capturing screenshots or saving waveform data.
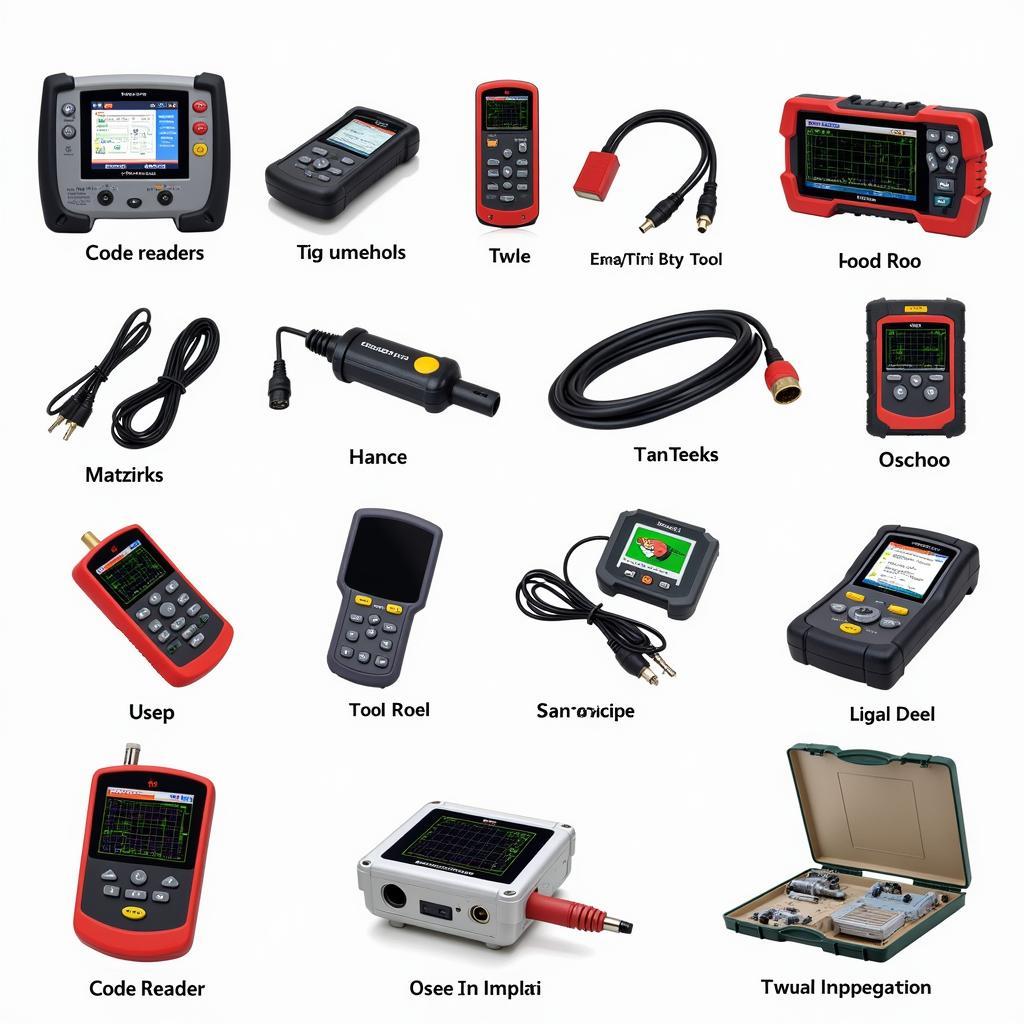 Various Diagnostic Tools in an Automotive Classroom
Various Diagnostic Tools in an Automotive Classroom
“Accurate data extraction is the foundation of effective diagnostics,” says John Miller, Senior Automotive Instructor at Apex Technical Institute. “Students need to master this skill to become proficient automotive technicians.”
Common Challenges in Test Extraction and Their Solutions
While extracting test results is generally straightforward, some challenges can arise:
- Software Compatibility: Ensure the diagnostic tool’s software is compatible with the vehicle’s onboard computer.
- Data Corruption: Use high-quality USB drives and avoid interrupting the data saving process to prevent corruption.
- Interpretation Errors: Proper training is essential to correctly interpret the extracted data.
“Understanding the nuances of each diagnostic tool is key,” adds Sarah Chen, Automotive Diagnostics Specialist at AutoTech Solutions. “Knowing the specific extraction procedures for each tool prevents errors and ensures accurate diagnosis.”
Conclusion
Mastering Classroom Diagnostic Tools Test Extract Instructions is vital for aspiring automotive technicians. By following the outlined steps and understanding the specific procedures for each tool, students can gain the necessary skills to diagnose and repair modern vehicles effectively. Contact ScanToolUS at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1615 S Laramie Ave, Cicero, IL 60804, USA for further assistance and to explore our range of diagnostic tools.
FAQ
- What is the OBD-II port? The OBD-II port is a standardized connector used to access a vehicle’s onboard computer.
- Why is vehicle identification important? Correct vehicle identification ensures the diagnostic tool retrieves the right information.
- What are DTCs? DTCs are codes stored in the vehicle’s computer, indicating specific malfunctions.
- How do I interpret extracted data? Training and experience are necessary to interpret the data correctly.
- What if the data is corrupted? Repeat the test and ensure a stable connection during data saving.
- Where can I find more information on diagnostic tools? Contact ScanToolUS for expert advice and support.
- What are the benefits of using classroom diagnostic tools? They allow students to gain hands-on experience in a controlled environment.