Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), the most common type of kidney cancer, often presents with subtle symptoms, making early diagnosis crucial for successful treatment. This guide explores the critical role of diagnostic tools in identifying and managing renal cell carcinoma.
Understanding the Importance of Early RCC Diagnosis
Early detection of renal cell carcinoma significantly improves patient prognosis. When discovered in its early stages, RCC is often treatable with minimally invasive procedures, leading to higher survival rates. Conversely, late-stage diagnosis often involves more complex treatments and a less optimistic outlook. Therefore, utilizing effective diagnostic tools is paramount in the fight against renal cell carcinoma.
Diagnostic Tools for Renal Cell Carcinoma: From Traditional to Cutting-Edge
Several diagnostic tools are employed to detect and evaluate renal cell carcinoma. These range from traditional imaging techniques to advanced biopsy procedures. Each method plays a vital role in painting a comprehensive picture of the disease.
Imaging Techniques: Visualizing the Unseen
Imaging techniques are the cornerstone of RCC diagnosis. They allow healthcare professionals to visualize the kidneys and surrounding structures, identifying suspicious masses and assessing their characteristics.
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive and readily available imaging modality, ultrasound is often the initial step in evaluating kidney abnormalities. While it can detect the presence of a mass, it may not be sufficient to definitively diagnose RCC.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the kidneys, offering valuable information about the size, shape, and location of tumors. They also help assess the extent of the disease and potential spread to other organs.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI utilizes magnetic fields and radio waves to generate high-resolution images, offering a more detailed view of soft tissues compared to CT scans. MRI is particularly useful in differentiating between benign and malignant kidney masses.
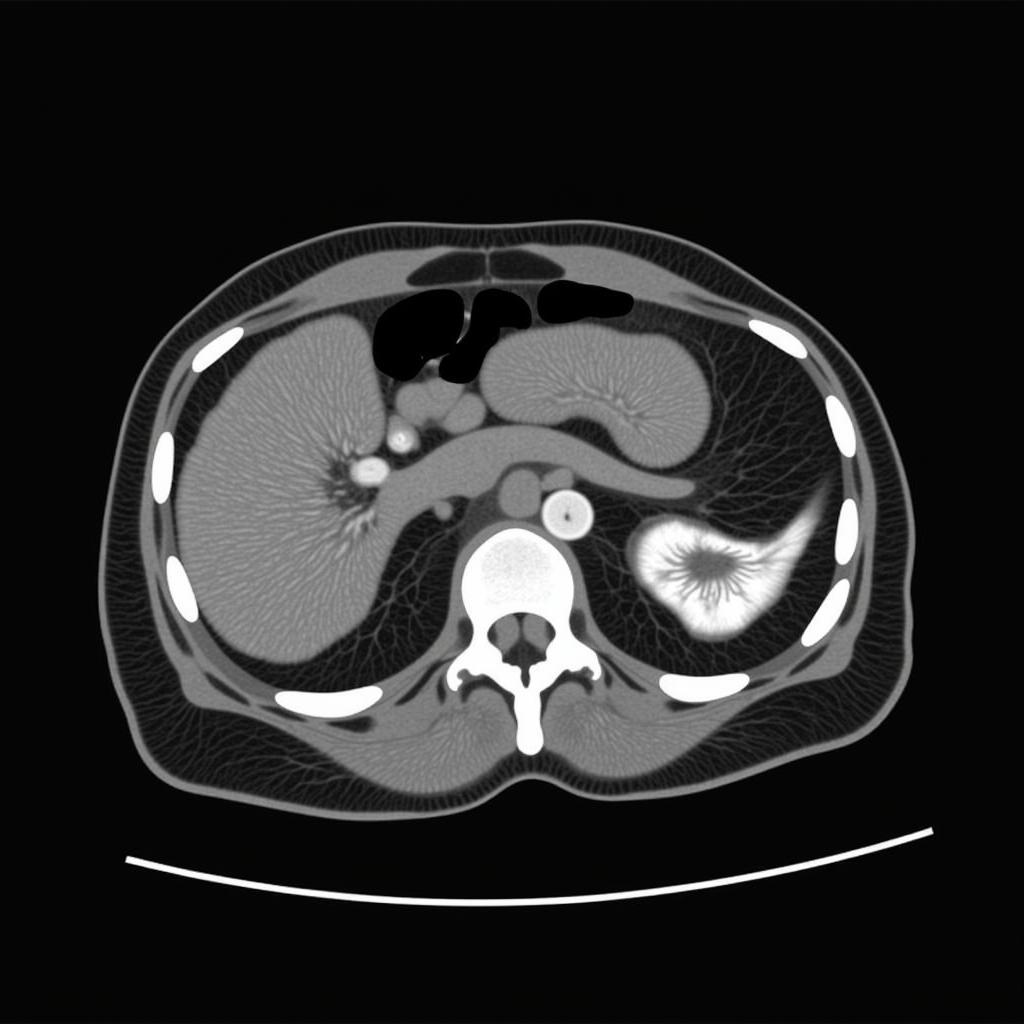 CT Scan for Renal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis
CT Scan for Renal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis
Biopsy: Confirming the Diagnosis
While imaging techniques provide valuable information, a biopsy is often necessary to confirm the diagnosis of RCC. A biopsy involves removing a small tissue sample from the suspicious area for microscopic examination. This procedure provides definitive confirmation of the presence of cancer cells.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA): A thin needle is inserted into the kidney to collect a sample of cells. This minimally invasive procedure is often performed under ultrasound or CT guidance.
- Core Needle Biopsy: A slightly larger needle is used to obtain a core of tissue, providing a more representative sample for analysis.
Blood and Urine Tests: Supporting the Diagnostic Process
Although not diagnostic on their own, blood and urine tests can provide supporting evidence and help monitor kidney function.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC can detect anemia, which is sometimes associated with RCC.
- Urinalysis: Urinalysis can identify blood in the urine (hematuria), a potential sign of kidney problems.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor About Renal Cell Carcinoma Diagnostic Tools?
When discussing Renal Cell Carcinoma Diagnostic Tools with your doctor, several key questions can help you gain a clear understanding of your situation and treatment options. These include:
- What diagnostic tests are recommended for my specific case?
- What are the risks and benefits of each test?
- How accurate are these tests in diagnosing RCC?
- What are the next steps if the tests are positive for RCC?
Navigating the Renal Cell Carcinoma Diagnostic Journey
The process of diagnosing renal cell carcinoma can be overwhelming. By understanding the available diagnostic tools and asking the right questions, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions and navigate this journey with confidence.
“Early detection is key in managing renal cell carcinoma,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a leading oncologist specializing in kidney cancer. “Utilizing advanced diagnostic tools allows us to identify and treat the disease in its earliest stages, significantly improving patient outcomes.”
Conclusion: The Power of Early Diagnosis with Renal Cell Carcinoma Diagnostic Tools
Renal cell carcinoma diagnostic tools play a crucial role in the fight against kidney cancer. By utilizing a combination of imaging techniques, biopsy procedures, and laboratory tests, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose and stage RCC, leading to more effective treatment strategies and improved patient outcomes. Remember, early detection is key. If you have any concerns about kidney cancer or are experiencing symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional immediately.
We encourage you to connect with ScanToolUS for further assistance and information. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1615 S Laramie Ave, Cicero, IL 60804, USA.
“Accurate staging is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan,” adds Dr. David Miller, a renowned nephrologist. “The information gleaned from diagnostic tools allows us to tailor treatment to each individual’s specific needs, optimizing their chances of success.”
FAQ
- What are the common symptoms of renal cell carcinoma?
- How is renal cell carcinoma staged?
- What are the treatment options for renal cell carcinoma?
- What is the survival rate for renal cell carcinoma?
- What are the risk factors for developing renal cell carcinoma?
- Are there any preventative measures for renal cell carcinoma?
- How often should I get screened for renal cell carcinoma?

